Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD: A Path to Freedom
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) affects millions of people worldwide, causing distressing and intrusive thoughts, as well as repetitive behaviors that can significantly impact daily life. While OCD may feel overwhelming, there is hope in the form of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), a highly effective treatment approach that has brought relief to countless individuals.
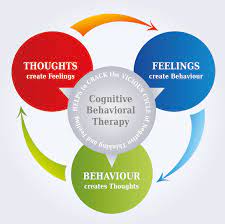
CBT is a psychological therapy that focuses on identifying and challenging unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. It aims to break the cycle of obsessions and compulsions by helping individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms. When it comes to OCD, CBT targets two main components: cognitive restructuring and exposure with response prevention.
Cognitive restructuring involves examining the thoughts and beliefs that drive obsessive thinking. It helps individuals recognize irrational or exaggerated fears and challenges the validity of these thoughts. Through this process, patients learn to reframe their thinking patterns, replacing negative or intrusive thoughts with more realistic and balanced ones.
Exposure with response prevention is another crucial aspect of CBT for OCD. This technique involves gradually exposing individuals to situations or triggers that typically provoke anxiety or compulsive behavior. The goal is to help patients confront their fears without engaging in their usual rituals or avoidance strategies. Over time, this exposure allows them to develop resilience and reduce the power these triggers hold over them.
One of the strengths of CBT for OCD is its collaborative nature. Therapists work closely with patients to create personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. This collaboration fosters a sense of empowerment as individuals actively participate in their own recovery journey.
A key element in CBT for OCD is homework assignments. These assignments encourage patients to practice new skills outside therapy sessions, reinforcing what they have learned in a real-world context. Homework might include exposure exercises, thought records, or behavioral experiments aimed at challenging unhelpful beliefs.
It’s important to note that CBT for OCD is not a quick fix. It requires time, commitment, and effort from both the therapist and the individual seeking treatment. However, the long-term benefits are worth it. Research has consistently shown that CBT is highly effective in reducing OCD symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
In addition to CBT, medication can also be used as part of an integrated treatment approach for OCD. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can help manage symptoms and support the effectiveness of therapy.
If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD, seeking professional help from a qualified therapist who specializes in CBT for OCD is crucial. They will provide guidance, support, and evidence-based techniques to help you regain control over your life.
Remember, OCD does not define you, and with the right tools and support, you can break free from its grip. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy offers a path to freedom by empowering individuals to challenge their thoughts, confront their fears, and reclaim their lives from the clutches of OCD.
Exploring the Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD is an evidence-based treatment that has been proven to be effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- CBT can help individuals identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts and develop new, more helpful ways of thinking and behaving.
- CBT helps individuals recognize their triggers for obsessive thoughts and learn how to manage them in a more productive way.
- CBT encourages individuals to set realistic goals and gradually face their fears in order to break the cycle of avoidance associated with OCD symptoms.
- Through CBT, individuals can gain insight into their condition, develop better coping skills, increase self-esteem, and learn how to maintain progress after treatment ends.
Challenges and Limitations of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD can be expensive and time-consuming, as it typically requires several sessions with a trained therapist.
- CBT may not work for everyone, and some individuals may find that the techniques are not effective in managing their OCD symptoms.
- CBT requires a great deal of effort and commitment from the patient to achieve positive results.
- People with severe OCD may have difficulty engaging in the cognitive restructuring techniques used in CBT, as they require them to confront their fears and anxieties head-on.
- The success of CBT relies heavily on the patient’s ability to follow through with homework assignments given by the therapist outside of session times, which can be difficult for some people to consistently do on their own.
- There is also a risk that patients will develop an unhealthy dependence on their therapists if they become too reliant on them for guidance or support during treatment sessions rather than developing self-help skills independently
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD is an evidence-based treatment that has been proven to be effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD: An Evidence-Based Path to Recovery
When it comes to treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as a highly effective and evidence-based treatment. With its proven track record, CBT offers hope for individuals seeking relief from the distressing symptoms of OCD.
Research consistently demonstrates the effectiveness of CBT in reducing OCD symptoms and improving overall quality of life. This evidence-based approach has been widely studied and validated, making it a recommended treatment by mental health professionals worldwide.
One of the key advantages of CBT for OCD is its focus on targeting specific thoughts and behaviors associated with the disorder. By addressing both cognitive processes and behavioral patterns, CBT provides individuals with practical tools to challenge their obsessions and compulsions head-on.
Through cognitive restructuring, individuals learn to identify and challenge irrational or exaggerated thoughts that fuel their OCD symptoms. By replacing these unhelpful thoughts with more realistic and balanced ones, patients gain a greater sense of control over their thinking patterns.
Additionally, exposure with response prevention is a crucial component of CBT for OCD. This technique allows individuals to gradually confront feared situations or triggers without engaging in their usual rituals or avoidance behaviors. Over time, this exposure helps reduce anxiety and diminishes the power that obsessions hold over them.
The evidence supporting CBT for OCD extends beyond just symptom reduction. Studies have shown that CBT also leads to improvements in overall functioning and quality of life. By addressing the core issues underlying OCD, individuals can experience long-lasting changes that positively impact various aspects of their lives.
Furthermore, CBT empowers individuals by providing them with practical skills they can apply independently outside therapy sessions. Through homework assignments and continued practice, patients develop resilience, self-awareness, and the ability to manage their symptoms effectively.
If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD, consider seeking professional help from a therapist trained in CBT for OCD. By utilizing this evidence-based treatment, you can gain the tools and support needed to reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and embark on a path towards recovery.
Remember, you are not alone in your journey. With Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD, there is hope for a brighter future where you can regain control over your thoughts and behaviors, leading to a more fulfilling and satisfying life.
CBT can help individuals identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts and develop new, more helpful ways of thinking and behaving.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven to be an invaluable tool in the treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). One significant benefit of CBT is its ability to help individuals identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts, ultimately leading to the development of new, more helpful ways of thinking and behaving.
For people with OCD, intrusive thoughts can be distressing and overwhelming. These thoughts often lead to compulsive behaviors that provide temporary relief but perpetuate the cycle of anxiety. CBT addresses this by assisting individuals in recognizing the patterns of negative thinking associated with their OCD symptoms.
Through CBT, individuals learn to identify and challenge these unhelpful thoughts. They work closely with a therapist to examine the evidence supporting these thoughts and explore alternative interpretations. This process helps individuals gain a more balanced perspective on their obsessions and reduces their distress.
Moreover, CBT equips individuals with practical strategies to develop new ways of thinking and behaving. By challenging irrational beliefs and replacing them with more realistic ones, people with OCD can break free from the grip of their obsessions. This shift in mindset empowers them to approach situations that once triggered anxiety with greater confidence and resilience.
CBT also focuses on behavioral changes by encouraging individuals to engage in activities that challenge their OCD symptoms. This exposure therapy allows them to confront their fears gradually while refraining from engaging in compulsions or avoidance behaviors. Over time, this process helps reduce anxiety and reinforces the understanding that these feared consequences are unlikely or even irrational.
By helping individuals identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts while developing new ways of thinking and behaving, CBT offers a powerful solution for those struggling with OCD. It provides them with practical tools to regain control over their lives and break free from the limitations imposed by their condition.
If you or someone you know is dealing with OCD, consider seeking help from a qualified therapist who specializes in CBT for OCD. With their guidance and support, you can embark on a transformative journey towards a more balanced and fulfilling life. Remember, change is possible, and CBT is here to help you challenge those unhelpful thoughts and embrace a brighter future.
CBT helps individuals recognize their triggers for obsessive thoughts and learn how to manage them in a more productive way.
Managing OCD Triggers: The Power of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can be incredibly distressing, with intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors that disrupt daily life. However, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a powerful solution by helping individuals recognize their triggers for obsessive thoughts and teaching them effective management strategies.
One of the key advantages of CBT for OCD is its focus on identifying triggers. Triggers are situations, objects, or thoughts that provoke obsessive thinking and lead to compulsive behaviors. By pinpointing these triggers, individuals gain valuable insight into the patterns that fuel their OCD.
Through CBT, individuals learn to recognize their triggers and understand how they contribute to the cycle of obsessions and compulsions. This awareness is crucial as it allows them to interrupt the automatic response and choose a more productive way of managing their thoughts.
CBT equips individuals with practical techniques to manage their triggers in a healthier manner. Therapists work collaboratively with patients to develop personalized strategies tailored to their specific triggers. These strategies may involve cognitive restructuring exercises, where individuals challenge irrational beliefs associated with their triggers. They also learn relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness to help manage anxiety when confronted with triggering situations.
By learning how to manage triggers effectively, individuals can break free from the cycle of obsession-compulsion and regain control over their lives. They become empowered to face triggering situations without resorting to unhealthy coping mechanisms or rituals that perpetuate OCD symptoms.
It’s important to remember that managing triggers is not about avoiding them altogether but rather developing resilience when faced with them. CBT helps individuals build skills and confidence in handling triggering situations head-on, reducing the power these triggers hold over them.
If you or someone you know struggles with OCD, consider exploring Cognitive Behavioral Therapy as a treatment option. With its focus on trigger recognition and management, CBT offers a pathway towards breaking free from obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. By learning how to manage triggers in a more productive way, individuals can reclaim their lives and move towards a future of greater freedom and well-being.
CBT encourages individuals to set realistic goals and gradually face their fears in order to break the cycle of avoidance associated with OCD symptoms.
Breaking the Cycle of Avoidance: How CBT Empowers Individuals with OCD
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) often leads individuals to engage in avoidance behaviors as a means of coping with their distressing thoughts and fears. However, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a powerful solution by encouraging individuals to set realistic goals and gradually face their fears. This approach helps break the cycle of avoidance associated with OCD symptoms, leading to significant improvements in overall well-being.
One of the core principles of CBT for OCD is to challenge avoidance behaviors head-on. Many individuals with OCD develop rituals or compulsions that temporarily alleviate anxiety but reinforce the underlying fears. CBT recognizes that avoidance only perpetuates the problem, making it essential to confront these fears instead.
Through CBT, individuals work collaboratively with their therapists to identify specific goals related to their OCD symptoms. These goals are realistic and achievable, taking into account each person’s unique circumstances and level of comfort. By setting these goals, individuals gain a sense of direction and purpose in their treatment journey.
CBT then guides individuals through a gradual exposure process. This involves facing feared situations or triggers in a controlled manner while refraining from engaging in compulsive behaviors or rituals. The exposure is done incrementally, starting with less anxiety-provoking situations and progressing towards more challenging ones over time.
By gradually facing their fears, individuals learn that their anxiety diminishes naturally without resorting to their usual coping mechanisms. This process helps them realize that they are capable of tolerating discomfort and that their feared outcomes are often exaggerated or unlikely to occur.
The power of gradual exposure lies in its ability to rewire the brain’s response patterns. With repeated exposure, the brain learns new associations between feared stimuli and reduced anxiety levels. As a result, individuals become less reliant on avoidance behaviors and gain confidence in facing future challenges.
CBT also equips individuals with valuable skills for managing anxiety and OCD symptoms. They learn various techniques, such as cognitive restructuring, which involves challenging and replacing irrational thoughts with more realistic ones. These skills empower individuals to take control of their thought processes and reduce the influence of OCD on their daily lives.
By breaking the cycle of avoidance, CBT offers individuals with OCD a chance to reclaim their lives from the grip of anxiety and fear. It encourages them to set realistic goals, face their fears gradually, and develop effective coping strategies. Through this process, individuals gain a renewed sense of empowerment, independence, and hope for a brighter future.
If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD, consider seeking help from a qualified therapist who specializes in CBT. With their guidance and support, you can embark on a transformative journey towards breaking free from avoidance behaviors and regaining control over your life. Remember that change is possible, and CBT can be the key to unlocking a future filled with resilience and well-being.
Through CBT, individuals can gain insight into their condition, develop better coping skills, increase self-esteem, and learn how to maintain progress after treatment ends.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD offers individuals a multitude of benefits, including gaining valuable insight into their condition, developing effective coping skills, boosting self-esteem, and learning how to sustain progress even after treatment concludes.
One of the primary advantages of CBT for OCD is the opportunity for individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their condition. Through therapy sessions, patients can explore the underlying causes and triggers of their obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. This insight helps them recognize patterns, identify irrational beliefs, and understand how these factors contribute to the maintenance of their OCD symptoms.
In addition to insight, CBT equips individuals with practical coping skills that they can utilize in their daily lives. Therapists work collaboratively with patients to teach them effective strategies for managing anxiety and resisting compulsions. By learning alternative ways to respond to intrusive thoughts or triggers, individuals can gradually reduce their reliance on compulsive behaviors and regain control over their lives.
Another significant benefit of CBT is its positive impact on self-esteem. OCD often leads individuals to feel shame, guilt, or embarrassment due to the nature of their obsessions and rituals. CBT helps challenge these negative self-perceptions by providing a supportive environment where patients can openly discuss their experiences without judgment. As individuals make progress in therapy by challenging their fears and reframing negative thoughts, they begin to build a stronger sense of self-worth and confidence.
Furthermore, CBT emphasizes the importance of maintaining progress even after treatment concludes. Therapists guide patients in developing relapse prevention strategies and teach them how to apply the skills they have learned independently. By equipping individuals with tools for long-term success, CBT empowers them to continue managing their symptoms effectively beyond the therapy room.
In summary, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD offers numerous advantages that extend beyond symptom reduction. Through CBT, individuals gain valuable insight into their condition, develop effective coping skills that empower them to resist compulsions, experience a boost in self-esteem, and learn how to maintain progress independently. This comprehensive approach ensures that individuals not only find relief from their OCD symptoms but also acquire the necessary tools to lead fulfilling lives long after therapy concludes.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD can be expensive and time-consuming, as it typically requires several sessions with a trained therapist.
Considering the Costs: The Expense and Time Commitment of CBT for OCD
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized as an effective treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), it’s important to acknowledge a potential drawback: the expense and time commitment involved. CBT for OCD typically requires multiple sessions with a trained therapist, which can be both financially and temporally demanding.
Therapy sessions with a qualified professional are an essential component of CBT for OCD, as they provide guidance, support, and evidence-based techniques to help individuals manage their symptoms effectively. However, these sessions come at a cost. Therapists who specialize in treating OCD often charge fees that may not be covered by insurance or may require out-of-pocket expenses. This financial aspect can be challenging for individuals with limited resources or those without comprehensive insurance coverage.
Furthermore, CBT for OCD is not a quick fix; it requires time and commitment. The therapy process typically involves regular sessions over several weeks or months. This ongoing commitment may pose challenges for individuals with busy schedules or limited availability due to work, family responsibilities, or other obligations.
However, it’s important to weigh these potential drawbacks against the long-term benefits of CBT for OCD. While the expense and time commitment can be significant, the positive impact on one’s quality of life is often profound. CBT has been shown to reduce OCD symptoms and improve overall well-being in numerous studies.
For those facing financial barriers, there may be options available to explore. Some therapists offer sliding scale fees based on income level or have programs that provide reduced-cost services. Additionally, community mental health centers or university clinics may offer more affordable options for CBT treatment.
It’s crucial to consider the potential benefits of investing in one’s mental health when evaluating the costs associated with CBT for OCD. The long-lasting improvements in symptom management, increased functionality, and enhanced quality of life that can result from successful therapy may outweigh the financial and time commitments in the long run.
If financial constraints or time limitations are a concern, it may be worthwhile to discuss these factors with a therapist or seek alternative resources. They can provide guidance on available options, potential financial assistance programs, or suggest self-help resources that can supplement therapy sessions.
Ultimately, while the expense and time commitment of CBT for OCD should be acknowledged, individuals should also consider the potential positive impact on their well-being. By investing in their mental health and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can take significant steps towards managing their OCD symptoms and improving their overall quality of life.
CBT may not work for everyone, and some individuals may find that the techniques are not effective in managing their OCD symptoms.
Exploring Limitations: CBT and OCD Treatment
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has long been recognized as a highly effective treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). However, it’s important to acknowledge that CBT may not work for everyone, and some individuals may find that the techniques are not as effective in managing their OCD symptoms.
While CBT has shown significant success rates in reducing OCD symptoms for many individuals, each person’s experience with the disorder is unique. There can be various factors that contribute to the limitations of CBT in certain cases. Let’s delve into a few reasons why CBT may not work for everyone with OCD:
- Treatment Resistance: Some individuals with OCD may have a resistance to treatment or struggle with engaging fully in therapy. This resistance can stem from various factors such as fear, skepticism, or difficulty embracing change. In such cases, the effectiveness of CBT techniques may be hindered by the individual’s unwillingness or inability to fully participate.
- Co-occurring Conditions: It’s not uncommon for individuals with OCD to also have co-occurring conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, or other mental health issues. These additional conditions can complicate treatment and impact the overall effectiveness of CBT. In such cases, a more comprehensive approach that addresses all underlying conditions may be necessary.
- Treatment Refinement: While CBT is a well-established therapeutic approach, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each person’s experience of OCD is unique, and what works for one individual might not work as effectively for another. It may require refinement of treatment strategies or exploration of alternative therapeutic approaches tailored to an individual’s specific needs.
- Severity and Complexity: The severity and complexity of an individual’s OCD symptoms can also impact the effectiveness of CBT. In cases where symptoms are particularly severe or deeply ingrained, additional interventions or adjunctive treatments might be necessary to achieve significant progress.
It’s essential to remember that the limitations of CBT for OCD do not imply that there are no alternative treatment options available. In cases where CBT may not be as effective, therapists can explore alternative therapeutic approaches, such as Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), or medication management, in conjunction with or instead of CBT.
Additionally, ongoing research and advancements in the field of OCD treatment continue to provide insights into new therapeutic modalities. It’s always advisable to consult with a qualified mental health professional who can assess your unique situation and guide you towards the most appropriate treatment options.
While CBT has proven highly effective for many individuals with OCD, it’s important to recognize that it may not be universally successful. By acknowledging these limitations and exploring alternative approaches, individuals can continue their journey towards finding relief from OCD symptoms and improving their overall well-being.
CBT requires a great deal of effort and commitment from the patient to achieve positive results.
The Commitment Conundrum: The Effort Required for CBT in OCD Treatment
When it comes to treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized as an effective approach. However, one con of CBT for OCD is the level of effort and commitment required from patients to achieve positive results.
CBT is not a passive form of therapy. It demands active participation and dedication from individuals seeking treatment. This commitment can be challenging, especially for those already feeling overwhelmed by the burdensome nature of OCD.
The process of CBT involves regular therapy sessions, typically spanning several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the condition. During these sessions, patients work closely with their therapists to identify and challenge their unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. They learn new coping strategies, engage in exposure exercises, and practice implementing healthier responses to their obsessions.
Outside of therapy sessions, patients are often assigned homework assignments that require them to apply what they have learned. These assignments may involve confronting feared situations or triggers without resorting to compulsions or avoidance behaviors. This continuous effort is essential for reinforcing new patterns of thinking and behavior.
While the effort required can be daunting, it’s important to remember that lasting change rarely comes without some level of dedication. Overcoming OCD requires persistence and a willingness to confront fears head-on. CBT provides individuals with tools and techniques that empower them in their journey towards recovery.
However, it’s crucial for therapists to acknowledge the potential challenges patients may face in maintaining this level of commitment throughout treatment. Therapeutic support should include understanding the individual’s limitations, providing encouragement during difficult moments, and helping them develop strategies for staying motivated.
It’s also worth noting that everyone progresses at their own pace in therapy. Some individuals may see significant improvements relatively quickly, while others may require more time and patience. The key is not to become discouraged but rather to focus on the gradual steps forward and celebrate each small victory along the way.
Ultimately, the effort and commitment required for CBT in OCD treatment are necessary investments in one’s well-being. While it may feel overwhelming at times, the potential rewards of reduced OCD symptoms, improved quality of life, and regained control over one’s thoughts and behaviors make it a worthwhile endeavor.
If you or someone you know is considering CBT for OCD, it’s important to have an open and honest discussion with a qualified therapist about the level of commitment required. Together, you can explore strategies to manage any potential challenges and develop a treatment plan that suits your needs and capabilities.
Remember, while the journey may be demanding, it is through perseverance and dedication that positive change can be achieved.
People with severe OCD may have difficulty engaging in the cognitive restructuring techniques used in CBT, as they require them to confront their fears and anxieties head-on.
Challenges of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Severe OCD: Confronting Fears Head-On
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized as an effective treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). However, it’s important to acknowledge that individuals with severe OCD may face unique challenges when engaging in the cognitive restructuring techniques used in CBT.
One of the primary goals of CBT for OCD is to help individuals recognize and challenge their irrational thoughts and beliefs. This process, known as cognitive restructuring, requires patients to confront their fears and anxieties head-on. While this approach can be highly beneficial for many individuals, those with severe OCD may find it extremely difficult to engage in this aspect of therapy.
For individuals with severe OCD, their fears and anxieties are often deeply ingrained and overwhelming. The thought of directly confronting these fears can evoke intense distress and trigger a cascade of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. This can make it challenging for them to actively participate in the cognitive restructuring exercises that are central to CBT.
Moreover, individuals with severe OCD may have developed extensive avoidance strategies or rituals as a way to manage their anxiety. These strategies provide temporary relief but reinforce the belief that avoiding or engaging in compulsions is necessary for managing their fears. As a result, breaking this cycle becomes more complicated when attempting cognitive restructuring techniques.
It’s important for therapists working with individuals who have severe OCD to be aware of these challenges and adapt their approach accordingly. They may need to start with less direct exposure exercises or employ gradual exposure techniques that allow patients to build up tolerance over time. Therapists must also provide a supportive and non-judgmental environment where patients feel safe expressing their fears and anxieties.
In some cases, therapists may need to explore alternative treatment approaches or consider integrating medication alongside therapy. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can help manage symptoms and reduce anxiety, making it easier for individuals with severe OCD to engage in cognitive restructuring techniques.
While the challenges of cognitive restructuring for severe OCD are significant, it’s crucial to remember that therapy is a collaborative process. With patience, understanding, and tailored strategies, therapists can work with individuals to find alternative ways to address their fears and anxieties. The goal is to gradually build resilience and empower patients to confront their OCD symptoms at a pace that feels manageable for them.
If you or someone you know is struggling with severe OCD, seeking professional help from a qualified therapist experienced in treating OCD is essential. They can provide the necessary guidance and support to navigate the unique challenges associated with severe OCD and work towards finding effective solutions for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
The success of CBT relies heavily on the patient’s ability to follow through with homework assignments given by the therapist outside of session times, which can be difficult for some people to consistently do on their own.
The Challenge of Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized as an effective treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). However, like any therapeutic approach, it is important to acknowledge that CBT has its limitations. One such challenge lies in the nature of homework assignments given by therapists, which can be difficult for some individuals to consistently complete on their own.
Homework assignments are an integral part of CBT for OCD. They serve as a bridge between therapy sessions, allowing individuals to practice and reinforce the skills they learn during therapy in real-life situations. These assignments often involve exposure exercises or challenging unhelpful thoughts and behaviors.
While homework assignments are designed to enhance progress and empower patients, some people may find it challenging to follow through consistently. Various factors can contribute to this difficulty. For instance, individuals with busy schedules or demanding responsibilities may struggle to find dedicated time for homework. Additionally, external stressors or life circumstances can make it harder for some individuals to prioritize and commit to completing the assignments.
In some cases, the nature of OCD itself can pose hurdles when it comes to completing homework. The disorder’s symptoms, such as perfectionism or fear of making mistakes, may lead individuals to avoid or procrastinate on their assignments due to anxiety or self-doubt. This avoidance behavior can hinder progress and limit the effectiveness of CBT.
It is essential for therapists to be aware of these challenges and work collaboratively with their patients to find strategies that promote consistent engagement with homework assignments. Therapists can provide support by breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable steps or adjusting the frequency and intensity of assignments based on individual needs.
Additionally, therapists can explore alternative approaches if traditional homework assignments prove difficult for a particular patient. This may involve finding creative ways to integrate therapeutic techniques into daily routines or exploring other forms of therapy that better suit the individual’s circumstances and preferences.
While the success of CBT for OCD relies, to some extent, on the patient’s ability to complete homework assignments, it is important to remember that progress can still be made even if challenges arise. Open communication between the therapist and patient is crucial in addressing any difficulties and finding alternative solutions that support the individual’s journey towards recovery.
In conclusion, while homework assignments in CBT for OCD can present challenges for some individuals, therapists can work collaboratively with their patients to overcome these obstacles. By adapting strategies and finding alternative approaches when necessary, therapists can ensure that treatment remains effective and tailored to each individual’s unique circumstances and needs.
There is also a risk that patients will develop an unhealthy dependence on their therapists if they become too reliant on them for guidance or support during treatment sessions rather than developing self-help skills independently
A Potential Con of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD: Dependency on Therapists
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven to be highly effective in treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), it is essential to acknowledge potential drawbacks. One such concern is the risk of patients developing an unhealthy dependence on their therapists.
In the therapeutic relationship, trust and support are vital components. Patients often rely on their therapists for guidance and reassurance during the treatment process, which is a natural part of therapy. However, there is a potential downside if individuals become overly reliant on their therapists for every decision or coping strategy.
When patients excessively depend on their therapists, it can hinder their progress in developing self-help skills. The goal of CBT is to empower individuals to become self-sufficient in managing their OCD symptoms and challenging unhelpful thoughts independently. By fostering self-reliance, patients can maintain long-term progress even after therapy concludes.
To mitigate this risk, therapists practicing CBT for OCD should actively encourage patients to take ownership of their recovery journey. They should emphasize the importance of practicing skills learned in therapy outside of sessions and gradually reducing reliance on therapist guidance over time. Therapists can provide resources and tools that promote independent problem-solving and self-reflection.
It’s crucial for patients to recognize that therapists are there to support them but ultimately aim to help them develop the skills needed to navigate life without constant therapeutic intervention. Building self-help skills empowers individuals to face challenges head-on and make progress toward long-term recovery.
Additionally, establishing a strong therapeutic alliance based on open communication is vital. Patients should feel comfortable discussing any concerns or questions they have about dependency during therapy sessions. Therapists can address these concerns by collaboratively setting goals that promote independence and regularly assessing progress toward those goals.
In summary, while CBT for OCD offers significant benefits, including symptom reduction and improved quality of life, there is a potential risk of patients developing an unhealthy dependence on their therapists. By actively promoting independence and self-help skills, therapists can help individuals strike a balance between relying on therapeutic support and cultivating their ability to manage their OCD symptoms autonomously.