Types of Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It can manifest in different forms, each with its own unique characteristics and causes. Understanding the types of insomnia can help individuals identify their specific sleep issues and seek appropriate treatment. Here are some common types of insomnia:
Acute Insomnia
Acute insomnia is a brief period of difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, typically triggered by stressful events such as exams, job interviews, or personal problems. It usually resolves on its own once the stressor is removed or managed.
Chronic Insomnia
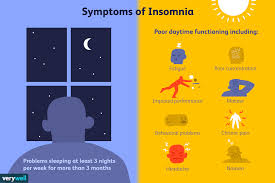
Chronic insomnia is characterized by ongoing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep for at least three nights a week for three months or more. It can be caused by various factors, including underlying health conditions, psychological issues, or poor sleep habits.
Onset Insomnia
Onset insomnia refers to difficulty falling asleep at the beginning of the night. Individuals with onset insomnia may lie awake in bed for an extended period before finally drifting off to sleep.
Maintenance Insomnia
Maintenance insomnia involves waking up multiple times during the night and having trouble returning to sleep. This type of insomnia can lead to fragmented and non-restorative sleep.
Comorbid Insomnia
Comorbid insomnia occurs alongside other medical or psychiatric conditions such as depression, anxiety, chronic pain, or sleep disorders like sleep apnea. Treating the underlying condition is essential in managing comorbid insomnia.
Psychophysiological Insomnia
Psychophysiological insomnia is often linked to excessive worry about not being able to fall asleep, leading to heightened arousal and conditioned arousal responses that perpetuate the cycle of poor sleep.
Idiopathic Insomnia
Idiopathic insomnia is a rare form of chronic insomnia that typically begins in childhood and persists into adulthood without an identifiable cause. It may be related to abnormalities in the brain’s sleep-wake regulation mechanisms.
If you are experiencing symptoms of any type of insomnia that are impacting your daily life and well-being, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment options.
Empowering Sleep Health: 8 Key Insights into Different Types of Insomnia
- Understanding the types of insomnia can help individuals identify and address their specific sleep issues.
- Differentiating between acute and chronic insomnia can guide appropriate treatment strategies based on the duration of symptoms.
- Recognizing onset and maintenance insomnia patterns can lead to targeted interventions to improve sleep quality.
- Identifying comorbid insomnia alongside other health conditions allows for comprehensive treatment plans addressing multiple issues.
- Awareness of psychophysiological insomnia helps individuals break the cycle of excessive worry and arousal that contribute to sleep difficulties.
- Acknowledging idiopathic insomnia as a rare but possible form of chronic sleep disorder promotes early intervention and management.
- Knowing the various types of insomnia encourages individuals to seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
- Being informed about the nuances of different types of insomnia empowers individuals to take control of their sleep health and overall well-being.
The Hidden Costs of Insomnia: 5 Ways It Impacts Health and Daily Life
- Insomnia can lead to daytime fatigue and decreased productivity.
- Persistent insomnia may contribute to mood disturbances such as irritability and anxiety.
- Chronic insomnia can increase the risk of developing other health conditions like cardiovascular disease and obesity.
- Difficulty concentrating and memory problems are common consequences of inadequate sleep due to insomnia.
- Insomnia can disrupt social relationships and daily functioning, impacting overall quality of life.
Understanding the types of insomnia can help individuals identify and address their specific sleep issues.
Understanding the types of insomnia can be incredibly beneficial for individuals as it enables them to pinpoint and tackle their specific sleep-related challenges effectively. By recognizing whether they are experiencing acute, chronic, onset, maintenance, comorbid, psychophysiological, or idiopathic insomnia, individuals can tailor their approach to managing their sleep issues. This knowledge empowers them to seek appropriate treatment or make lifestyle adjustments that target the root cause of their insomnia, ultimately leading to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
Differentiating between acute and chronic insomnia can guide appropriate treatment strategies based on the duration of symptoms.
Understanding the distinction between acute and chronic insomnia is crucial as it can guide healthcare providers in tailoring appropriate treatment strategies based on the duration of symptoms. Acute insomnia, typically triggered by short-term stressors, often resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed. In contrast, chronic insomnia, characterized by persistent sleep difficulties lasting for at least three months, may require more targeted interventions to address underlying health conditions, psychological factors, or poor sleep habits. By identifying whether insomnia is acute or chronic, healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that aim to effectively manage and alleviate the specific challenges faced by individuals experiencing different types of sleep disturbances.
Recognizing onset and maintenance insomnia patterns can lead to targeted interventions to improve sleep quality.
Recognizing onset and maintenance insomnia patterns can be a significant advantage as it allows for targeted interventions to enhance sleep quality. By identifying whether the difficulty lies in falling asleep at the beginning of the night (onset insomnia) or in waking up multiple times during the night and struggling to return to sleep (maintenance insomnia), individuals can tailor their approach to address specific sleep challenges. This targeted intervention approach increases the likelihood of implementing effective strategies that directly tackle the root causes of sleep disturbances, ultimately leading to improved overall sleep quality and better restorative rest.
Identifying comorbid insomnia alongside other health conditions allows for comprehensive treatment plans addressing multiple issues.
Identifying comorbid insomnia alongside other health conditions allows for comprehensive treatment plans addressing multiple issues. By recognizing the interconnected nature of insomnia with underlying medical or psychiatric conditions such as depression, anxiety, chronic pain, or sleep disorders, healthcare providers can develop holistic approaches that target not only the symptoms of insomnia but also the root causes contributing to sleep disturbances. This integrated approach not only improves sleep quality but also enhances overall health and well-being by addressing the complex interplay between different health issues.
Awareness of psychophysiological insomnia helps individuals break the cycle of excessive worry and arousal that contribute to sleep difficulties.
Awareness of psychophysiological insomnia plays a crucial role in helping individuals break the cycle of excessive worry and arousal that contribute to sleep difficulties. By understanding the connection between their thoughts, emotions, and sleep patterns, individuals can actively work on reducing anxiety and stress levels that may be hindering their ability to fall asleep. Recognizing the impact of psychological factors on insomnia empowers individuals to implement relaxation techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, and other strategies to promote a more restful and rejuvenating sleep experience. This increased awareness fosters a proactive approach to managing psychophysiological insomnia and ultimately supports better overall sleep health.
Acknowledging idiopathic insomnia as a rare but possible form of chronic sleep disorder promotes early intervention and management.
Acknowledging idiopathic insomnia as a rare but possible form of chronic sleep disorder promotes early intervention and management. By recognizing the existence of this specific type of insomnia, healthcare professionals and individuals experiencing persistent sleep difficulties can seek timely evaluation and appropriate treatment. Early intervention not only helps in addressing the symptoms of idiopathic insomnia but also prevents potential long-term consequences on physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Educating the public about this less common form of chronic sleep disorder raises awareness and encourages proactive steps towards better sleep health.
Knowing the various types of insomnia encourages individuals to seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
Understanding the diverse spectrum of insomnia types serves as a crucial proponent in motivating individuals to pursue professional assistance for precise diagnosis and tailored treatment. By familiarizing themselves with the distinct characteristics and underlying causes of different insomnia variations, individuals are empowered to recognize their specific sleep challenges and engage with healthcare providers to receive personalized care that addresses their unique needs effectively. This knowledge not only facilitates early intervention and management of insomnia but also promotes better overall sleep health and quality of life.
Being informed about the nuances of different types of insomnia empowers individuals to take control of their sleep health and overall well-being.
Being informed about the nuances of different types of insomnia empowers individuals to take control of their sleep health and overall well-being. By understanding the specific characteristics and causes of various types of insomnia, individuals can identify their own sleep issues more accurately and seek targeted treatment strategies. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions about lifestyle changes, therapy options, and behavioral modifications that can improve their sleep quality and contribute to better physical and mental health outcomes. Empowerment through education plays a crucial role in managing insomnia effectively and promoting a restful night’s sleep.
Insomnia can lead to daytime fatigue and decreased productivity.
Insomnia can have a detrimental impact on daytime functioning, as it often leads to persistent fatigue and decreased productivity. When individuals do not get adequate restorative sleep, they may experience difficulty concentrating, making decisions, and staying alert during the day. This can result in decreased work performance, impaired cognitive function, and an overall sense of lethargy that hinders daily activities. Chronic sleep deprivation due to insomnia can also weaken the immune system, increase the risk of accidents, and negatively affect mental health. It is essential to address insomnia promptly to prevent its negative consequences on overall well-being and quality of life.
Persistent insomnia may contribute to mood disturbances such as irritability and anxiety.
Persistent insomnia, characterized by ongoing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep for an extended period, can have detrimental effects on mental health. One significant con of persistent insomnia is its potential to contribute to mood disturbances such as irritability and anxiety. The chronic sleep deprivation and disruption of the sleep-wake cycle associated with persistent insomnia can lead to increased emotional sensitivity, heightened stress responses, and difficulty regulating emotions. Individuals experiencing persistent insomnia may find themselves more prone to irritability, mood swings, and feelings of anxiety, impacting their overall quality of life and well-being. Addressing persistent insomnia through proper treatment and management strategies is crucial in mitigating these mood disturbances and promoting mental wellness.
Chronic insomnia can increase the risk of developing other health conditions like cardiovascular disease and obesity.
Chronic insomnia, characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, poses a significant health risk beyond just sleep disturbances. Studies have shown that chronic insomnia can contribute to the development of other serious health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and obesity. The ongoing sleep deprivation and disruption in the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle associated with chronic insomnia can lead to systemic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic dysregulation, all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular issues and weight gain. Addressing chronic insomnia through proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial not only for improving sleep quality but also for reducing the potential impact on overall health and well-being.
Difficulty concentrating and memory problems are common consequences of inadequate sleep due to insomnia.
Difficulty concentrating and memory problems are prevalent consequences of inadequate sleep resulting from insomnia. When individuals do not get enough restorative sleep, their cognitive functions are significantly affected. The brain requires sufficient sleep to consolidate memories and process information effectively. Insomnia disrupts this crucial process, leading to difficulties in focusing, retaining information, and recalling memories. Persistent sleep deprivation can impair learning abilities, problem-solving skills, and overall cognitive performance, impacting both personal and professional aspects of one’s life. Managing insomnia and improving sleep quality are essential steps in enhancing concentration and memory functions.
Insomnia can disrupt social relationships and daily functioning, impacting overall quality of life.
Insomnia can significantly disrupt social relationships and daily functioning, ultimately affecting one’s overall quality of life. The persistent lack of adequate sleep can lead to irritability, mood swings, difficulty concentrating, and reduced energy levels, making it challenging to engage effectively in social interactions and daily tasks. The strain caused by insomnia on personal relationships due to fatigue and emotional instability can also contribute to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Additionally, the cognitive impairment resulting from sleep deprivation can impact work performance and decision-making abilities, further diminishing the individual’s overall well-being and satisfaction with life.