Excessive Drinking: Understanding the Risks and Finding Balance
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s not uncommon for individuals to turn to alcohol as a means of relaxation or escape. While moderate drinking can be enjoyed responsibly, excessive drinking can have serious consequences on our physical and mental well-being. It’s important to understand the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption and find a healthy balance that promotes overall wellness.
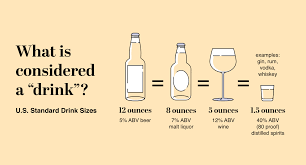
Excessive drinking, also known as heavy or binge drinking, is defined as consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short period or regularly consuming high quantities over time. This behavior can lead to a range of health problems, both immediate and long-term.
One immediate risk of excessive drinking is impaired judgment and coordination. Alcohol affects our cognitive abilities, making it more difficult to make rational decisions and increasing the likelihood of accidents or injuries. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to blackouts, memory loss, and even alcohol poisoning, which can be life-threatening.
Long-term effects of excessive drinking are even more concerning. Prolonged heavy drinking can lead to liver damage, including fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. These conditions can significantly impact liver function and may even require a liver transplant. Excessive alcohol consumption is also linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Moreover, excessive drinking takes a toll on our mental health. Alcohol is a depressant that affects the brain’s neurotransmitters responsible for mood regulation. While it may initially provide temporary relief from stress or anxiety, regular heavy drinking can worsen these conditions over time. It can contribute to the development of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety disorders.
Recognizing the signs of excessive drinking is crucial for intervention and seeking help when needed. Some common signs include neglecting responsibilities due to alcohol use, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when attempting to stop or cut back on drinking, developing tolerance (needing more alcohol to achieve the same effect), and continuing to drink despite negative consequences on relationships and personal well-being.
If you find yourself struggling with excessive drinking, it’s essential to seek support. There are numerous resources available, such as counseling services, support groups, and treatment programs that can provide guidance and assistance in overcoming alcohol addiction. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of strength, and there are people ready to support you on your journey towards a healthier lifestyle.
Finding a balance with alcohol consumption is key to maintaining overall well-being. It’s important to be mindful of the recommended guidelines for moderate drinking, which suggest no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. Additionally, it’s crucial to take regular breaks from alcohol consumption and prioritize other activities that promote physical and mental wellness.
In conclusion, excessive drinking poses significant risks to our health and well-being. It’s crucial to understand these risks, recognize the signs of problematic drinking, and seek help when needed. By finding a healthy balance with alcohol consumption and prioritizing our overall wellness, we can lead happier, healthier lives.
7 Frequently Asked Questions About Excessive Drinking
- What are the health risks of excessive drinking?
- How do I know if I’m drinking too much?
- How can I reduce my alcohol consumption?
- What are some signs of alcohol abuse?
- How can I help a friend or family member who is struggling with alcohol use disorder (AUD)?
- Are there any treatments for AUD?
- What should I do if I think someone has an alcohol problem?
What are the health risks of excessive drinking?
Excessive drinking poses numerous health risks that can have both immediate and long-term consequences. Here are some of the key health risks associated with heavy or binge drinking:
- Liver Damage: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver diseases such as fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. These conditions can impair liver function, cause inflammation, scarring, and even liver failure.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Heavy drinking is linked to an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), and stroke. Alcohol can raise blood pressure levels and contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries, which can lead to heart-related issues.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of developing various types of cancer, including mouth, throat, esophagus, liver, breast, and colorectal cancer. Alcohol metabolizes into acetaldehyde—a known carcinogen—which can damage DNA and promote tumor growth.
- Mental Health Disorders: Heavy drinking is closely linked to mental health problems such as depression and anxiety disorders. Alcohol acts as a depressant on the central nervous system and disrupts brain chemistry over time, potentially exacerbating existing mental health conditions or leading to new ones.
- Weakened Immune System: Excessive alcohol intake weakens the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases effectively. This makes individuals more susceptible to illnesses like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and other respiratory infections.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Alcohol interferes with nutrient absorption in the digestive system and impairs the body’s ability to utilize essential vitamins and minerals properly. This can lead to malnutrition and deficiencies in vital nutrients like vitamin B12, folate, thiamine (vitamin B1), vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, and others.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Alcohol impairs coordination, judgment, reaction time, and overall cognitive function. This significantly increases the risk of accidents, including motor vehicle accidents, falls, burns, and other unintentional injuries.
- Alcohol Poisoning: Consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short period can result in alcohol poisoning. This is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition characterized by confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow breathing, irregular heartbeat, and unconsciousness.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Excessive drinking can cause inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis), ulcers, acid reflux (GERD), and pancreatitis—painful inflammation of the pancreas.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to sexual dysfunction in both men and women. It may contribute to erectile dysfunction in men and disrupt menstrual cycles and fertility in women.
It’s important to note that these health risks can vary depending on factors such as individual susceptibility, genetic predisposition, overall health status, and patterns of alcohol consumption. If you or someone you know is struggling with excessive drinking or alcohol addiction, seeking professional help is crucial for support and guidance towards a healthier lifestyle.
How do I know if I’m drinking too much?
Knowing if you’re drinking too much can be a subjective assessment, but there are several signs and guidelines that can help you evaluate your alcohol consumption. Here are some indicators that may suggest you’re drinking excessively:
- Frequency: Do you find yourself drinking alcohol regularly, such as daily or multiple times a week? Consistently consuming alcohol can be a sign of excessive drinking.
- Quantity: Are you consuming large amounts of alcohol in a single session? Binge drinking, typically defined as consuming four or more drinks for women and five or more drinks for men within about two hours, is considered excessive.
- Loss of Control: Do you struggle to limit the amount of alcohol you consume once you start drinking? Difficulty stopping or controlling the amount of alcohol consumed is a common sign of problematic drinking.
- Dependence: Have you developed a tolerance to alcohol, requiring more drinks to achieve the desired effect? Do you experience withdrawal symptoms when attempting to cut back or stop drinking? These could indicate an increasing dependence on alcohol.
- Neglected Responsibilities: Has your alcohol consumption started to interfere with your daily responsibilities, such as work, relationships, or personal obligations? Neglecting important aspects of your life due to alcohol use is a red flag.
- Health Issues: Are you experiencing physical or mental health problems related to your alcohol consumption? Alcohol abuse can lead to various health issues like liver damage, cardiovascular problems, mental health disorders, and more.
- Relationship Strain: Has your drinking caused conflicts in your relationships with family members, friends, or colleagues? Excessive drinking can strain personal connections and lead to social consequences.
It’s important to remember that these indicators are not definitive proof of excessive drinking but rather warning signs that prompt further evaluation. If you have concerns about your alcohol consumption and its impact on your life, consider reaching out for professional help. Healthcare providers and addiction specialists can provide guidance and support tailored to your specific situation.
Ultimately, listening to your own instincts and being honest with yourself about your alcohol consumption is crucial. If you suspect that your drinking habits may be problematic, it’s always better to seek assistance sooner rather than later.
How can I reduce my alcohol consumption?
Reducing alcohol consumption can be a positive step towards improving your overall health and well-being. Here are some strategies that can help you reduce your alcohol intake:
- Set clear goals: Start by setting specific and realistic goals for yourself. Determine how many days a week you want to abstain from alcohol or set a limit on the number of drinks you’ll have on certain occasions.
- Identify triggers: Recognize the situations, emotions, or social settings that tend to lead to excessive drinking for you. By identifying these triggers, you can develop strategies to avoid or manage them more effectively.
- Find healthier alternatives: Replace alcoholic beverages with non-alcoholic options such as mocktails, herbal teas, infused water, or sparkling water with fruit garnishes. Having enjoyable alternatives can help reduce the desire for alcohol.
- Practice mindful drinking: Be present and aware of your consumption while drinking. Sip slowly and savor the taste rather than consuming alcoholic beverages quickly. This approach helps you become more conscious of how much you’re drinking and may naturally lead to reduced intake.
- Seek support: Reach out to friends, family members, or support groups who can provide encouragement and understanding during your journey to reduce alcohol consumption. Consider joining organizations like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor specializing in addiction.
- Engage in alternative activities: Find new hobbies, exercise regularly, explore creative outlets, or participate in activities that don’t revolve around alcohol consumption. Engaging in fulfilling activities can help distract from cravings and create healthier habits.
- Create a supportive environment: Surround yourself with individuals who respect your decision to reduce alcohol consumption and encourage healthier choices. Avoid environments where excessive drinking is prevalent if possible.
- Practice stress management techniques: Alcohol is often used as a coping mechanism for stress relief. Explore alternative stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, journaling, or seeking professional help to develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Track your progress: Keep a journal or use a mobile app to track your alcohol consumption. This can help you stay accountable and provide insights into patterns and triggers that may need further attention.
- Celebrate milestones: Celebrate your achievements along the way. Reward yourself for reaching specific goals, such as going a month without alcohol or successfully moderating your intake. Treat yourself with non-alcoholic rewards that align with your interests and hobbies.
Remember, reducing alcohol consumption is a personal journey, and it’s important to be patient and kind to yourself throughout the process. If you find it challenging to reduce your alcohol intake on your own, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance from healthcare providers or addiction specialists who can provide tailored support.
What are some signs of alcohol abuse?
Recognizing the signs of alcohol abuse is important in order to identify potential problems and seek appropriate help. Here are some common signs that may indicate alcohol abuse:
- Increased tolerance: Needing to consume larger amounts of alcohol to achieve the desired effect or experiencing diminished effects from the same amount.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Experiencing physical or psychological symptoms when attempting to stop drinking or cutting back, such as tremors, sweating, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, nausea, or hallucinations.
- Neglecting responsibilities: Prioritizing alcohol consumption over work, school, family obligations, or other important responsibilities.
- Loss of control: Being unable to limit the amount of alcohol consumed or consistently exceeding self-imposed limits.
- Failed attempts to quit or cut back: Repeatedly trying and failing to control or stop drinking despite negative consequences and a desire to do so.
- Increased time spent drinking: Spending significant amounts of time obtaining alcohol, consuming it, and recovering from its effects.
- Neglected hobbies and activities: Losing interest in previously enjoyed activities and hobbies in favor of drinking.
- Relationship problems: Experiencing conflicts with family members, friends, or partners due to alcohol-related behaviors such as arguments, aggression, or neglect.
- Continued use despite negative consequences: Persisting in drinking even when it leads to physical health issues (e.g., liver problems) or mental health problems (e.g., depression).
- Legal issues: Facing legal problems related to alcohol consumption such as DUI (driving under the influence), public intoxication charges, or other alcohol-related offenses.
It’s important to note that everyone’s situation is unique and that these signs may vary from person to person. If you notice these signs in yourself or someone you know, it may be beneficial to seek support from healthcare professionals, counselors specializing in addiction treatment, support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), or other resources available in your community.
How can I help a friend or family member who is struggling with alcohol use disorder (AUD)?
Supporting a friend or family member who is struggling with Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) can be challenging, but your support and understanding can make a significant difference in their journey towards recovery. Here are some ways you can help:
- Educate yourself: Learn about AUD, its signs and symptoms, and the available treatment options. Understanding the nature of the disorder will enable you to provide informed support.
- Offer non-judgmental support: Approach your loved one with empathy and compassion, avoiding judgment or criticism. Let them know that you are there for them and that you care about their well-being.
- Encourage open communication: Create a safe space for your loved one to talk about their struggles without fear of judgment or repercussions. Listen actively and validate their feelings.
- Express concern: Share your observations about their drinking behavior in a caring manner. Use “I” statements to express how their drinking affects you or others around them without blaming or accusing them.
- Encourage professional help: Suggest seeking professional assistance from healthcare providers, therapists, or addiction specialists who can provide guidance and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Offer practical assistance: Help your loved one find resources, such as treatment centers, support groups, or counseling services in their area. Offer to accompany them to appointments if they feel comfortable with it.
- Avoid enabling behaviors: While supporting your loved one, it’s essential not to enable their drinking habits by making excuses for them or covering up the consequences of their actions.
- Set boundaries: Establish clear boundaries regarding what behavior you are willing and unwilling to tolerate due to their drinking habits. Communicate these boundaries calmly and assertively.
- Encourage healthy activities: Suggest engaging in alternative activities that promote physical and mental well-being, such as exercise, hobbies, or spending quality time together without alcohol involved.
- Take care of yourself: Supporting someone with AUD can be emotionally draining. Remember to prioritize your own well-being by seeking support for yourself, setting limits on your involvement, and practicing self-care.
Remember, recovery from AUD is a complex process that takes time and commitment. Your role as a supportive friend or family member is essential, but ultimately, the decision to seek help and change lies with the individual struggling with AUD. Be patient, understanding, and continue to offer your support throughout their journey towards recovery.
Are there any treatments for AUD?
Yes, there are several treatments available for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD). The appropriate treatment for AUD may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and the severity of their condition. Here are some common treatment options:
- Detoxification: For individuals with severe alcohol dependence, a medically supervised detoxification process may be necessary to manage withdrawal symptoms safely. This process typically takes place in a specialized facility or hospital.
- Counseling and Therapy: Various counseling and therapy approaches can be beneficial in treating AUD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and change unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors related to alcohol use. Motivational interviewing focuses on enhancing motivation to make positive changes in drinking habits. Family therapy can also play a crucial role in addressing underlying family dynamics that contribute to alcohol misuse.
- Medications: Certain medications can aid in the treatment of AUD by reducing cravings or making alcohol consumption less pleasurable. These medications include naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if medication is appropriate for an individual’s specific situation.
- Support Groups: Participating in support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or other mutual-help programs can provide valuable peer support, guidance, and accountability throughout the recovery journey.
- Residential Treatment Programs: In cases where AUD is severe or accompanied by other mental health conditions, residential treatment programs may be recommended. These programs offer intensive therapy, counseling, medical supervision, and support within a structured environment.
- Holistic Approaches: Some individuals find benefit from complementary therapies such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, acupuncture, or art therapy as part of their overall treatment plan.
It’s important to note that recovery from AUD is a lifelong process, and different individuals may respond differently to various treatments. Seeking professional help from addiction specialists or healthcare providers who specialize in substance abuse is crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses the unique needs and circumstances of each individual.
What should I do if I think someone has an alcohol problem?
If you suspect that someone you know has an alcohol problem, it’s important to approach the situation with care and concern. Here are some steps you can take to help them:
- Educate yourself: Learn about alcohol addiction, its signs and symptoms, and the available treatment options. Understanding the nature of the problem will enable you to provide better support.
- Choose the right time and place: Find a suitable moment when both of you are calm and can have a private conversation without distractions or interruptions.
- Express your concerns: Approach the person in a non-judgmental and compassionate manner. Express your worries about their well-being, using “I” statements to avoid sounding accusatory. For example, say, “I’ve noticed that you’ve been drinking heavily lately, and I’m concerned about your health.”
- Provide specific examples: Share specific instances where their drinking has had negative consequences on their life or relationships. This can help them see the impact of their behavior.
- Offer support: Let them know that you are there for them and willing to support them through their journey towards recovery. Encourage them to seek professional help from a healthcare provider or addiction specialist.
- Avoid enabling behaviors: While offering support, it’s crucial not to enable their drinking habits by making excuses for their behavior or covering up the consequences of their actions.
- Encourage treatment options: Inform them about various treatment options available, such as counseling, therapy, support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), or rehabilitation programs. Offer to assist in finding resources or accompany them to appointments if they’re comfortable with it.
- Be patient and understanding: Recovery is a challenging process, and relapses may occur along the way. Encourage perseverance while being patient and understanding during setbacks.
- Take care of yourself: Supporting someone with an alcohol problem can be emotionally draining. Remember to prioritize your own well-being by seeking support from friends, family, or support groups for individuals affected by someone’s addiction.
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle: Promote activities and hobbies that don’t involve alcohol. Encourage them to engage in physical exercise, pursue their interests, and spend time with supportive friends and family members.
Remember, you cannot force someone to change or seek help if they are not ready. However, by expressing your concern and providing support, you can play a significant role in encouraging them to acknowledge their problem and take steps towards recovery.