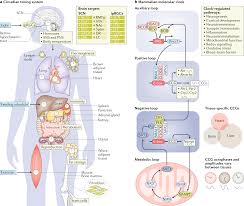
Our bodies operate on a natural internal clock known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates our sleep-wake cycle, hormone production, and other essential bodily functions. When this internal clock is disrupted or out of sync, it can lead to a circadian rhythm disorder, affecting our overall health and well-being.
There are several types of circadian rhythm disorders, with the most common being delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD), advanced sleep phase disorder (ASPD), irregular sleep-wake rhythm disorder, and shift work sleep disorder. Each of these disorders has its own unique characteristics and impacts on an individual’s daily life.
Delayed sleep phase disorder is characterized by a delayed onset of sleep and waking times, making it difficult for individuals to fall asleep at a conventional bedtime and wake up early for work or school. On the other hand, advanced sleep phase disorder causes individuals to fall asleep and wake up much earlier than desired, leading to difficulties in staying awake during evening activities.
Irregular sleep-wake rhythm disorder disrupts the normal 24-hour sleep-wake cycle, resulting in fragmented and inconsistent periods of sleep throughout the day and night. This can significantly impact an individual’s ability to maintain a regular daily schedule and may lead to excessive daytime sleepiness.
Shift work sleep disorder is commonly seen in individuals who work non-traditional hours or rotating shifts. The constant disruption of their natural circadian rhythm due to irregular work schedules can result in difficulties sleeping during the day and staying awake at night, leading to chronic fatigue and decreased cognitive function.
Managing circadian rhythm disorders often involves a combination of behavioral changes, light therapy, melatonin supplements, and in some cases, medication. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleeping environment, avoiding stimulants close to bedtime, and exposing oneself to natural light during the day can help regulate the circadian rhythm and improve overall sleep quality.
If you suspect that you may have a circadian rhythm disorder impacting your daily life, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your specific needs. By addressing underlying issues related to your circadian rhythm, you can optimize your health and well-being by achieving better quality sleep and improved overall functioning.
Understanding Circadian Rhythm Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
- What causes circadian rhythm disorder?
- What disrupts our circadian rhythm?
- What are the side effects of a disrupted circadian rhythm?
- How do you fix circadian rhythm disorder?
- What is an example of a circadian rhythm disorder?
- How do I reset my circadian rhythm?
- What are the symptoms of a circadian rhythm disorder?
What causes circadian rhythm disorder?
Circadian rhythm disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including disruptions to the body’s internal clock due to irregular work schedules, jet lag from travel across time zones, certain medical conditions like sleep apnea or depression, and lifestyle habits such as excessive screen time before bed or inconsistent sleep patterns. Environmental factors such as exposure to artificial light at night and lack of natural light during the day can also play a role in disrupting the circadian rhythm. Additionally, genetic predispositions may contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to circadian rhythm disorders. Understanding the potential causes of circadian rhythm disorder is crucial in identifying effective strategies for managing and improving one’s sleep-wake cycle for better overall health and well-being.
What disrupts our circadian rhythm?
Various factors can disrupt our circadian rhythm, leading to circadian rhythm disorders. One common disruptor is exposure to artificial light, especially blue light emitted by electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers. This type of light can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, making it harder for us to fall asleep at night. Irregular sleep schedules, shift work, jet lag from travel across time zones, certain medications, and underlying health conditions can also interfere with our circadian rhythm. By understanding these disruptors and making lifestyle adjustments such as limiting screen time before bed, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and creating a sleep-friendly environment, we can better support our body’s natural internal clock for improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
What are the side effects of a disrupted circadian rhythm?
Disrupted circadian rhythm can have a range of side effects that impact both physical and mental health. Common side effects include fatigue, difficulty concentrating, mood disturbances such as irritability or depression, impaired memory function, weakened immune system leading to increased susceptibility to illnesses, digestive issues, and disruptions in hormone regulation. Long-term consequences of a disrupted circadian rhythm may also include an increased risk of chronic conditions like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. It is crucial to address and manage circadian rhythm disorders promptly to mitigate these side effects and promote overall well-being.
How do you fix circadian rhythm disorder?
To address circadian rhythm disorder and restore a healthy sleep-wake cycle, several strategies can be implemented. One effective approach is to establish a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Exposure to natural light during the day and minimizing exposure to artificial light, especially blue light from screens, close to bedtime can help regulate the body’s internal clock. Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques before bedtime, such as deep breathing or meditation, can promote better sleep quality. In some cases, consulting with a healthcare provider or sleep specialist may be necessary to explore further treatment options like light therapy, melatonin supplements, or cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I). By making these lifestyle adjustments and seeking appropriate medical guidance, individuals can take steps towards fixing circadian rhythm disorder and improving their overall sleep patterns and well-being.
What is an example of a circadian rhythm disorder?
An example of a circadian rhythm disorder is delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD). Individuals with DSPD experience a significant delay in their sleep-wake cycle, making it challenging for them to fall asleep at a conventional bedtime and wake up early in the morning. This results in a mismatch between their internal body clock and the demands of their daily schedule, leading to difficulties in maintaining regular sleep patterns and often causing disruptions in daily functioning and productivity. DSPD can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting their performance at work or school, social interactions, and overall well-being.
How do I reset my circadian rhythm?
Resetting your circadian rhythm involves making gradual adjustments to your sleep-wake cycle to align it with your desired schedule. One effective way to reset your circadian rhythm is by establishing a consistent bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends. Exposure to natural light in the morning and limiting exposure to bright lights in the evening can help regulate your body’s internal clock. Avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronic devices close to bedtime can also promote better sleep quality. Additionally, engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can aid in resetting your circadian rhythm and improving overall sleep patterns.
What are the symptoms of a circadian rhythm disorder?
Individuals with circadian rhythm disorders may experience a range of symptoms that disrupt their sleep-wake cycle and daily functioning. Common symptoms of circadian rhythm disorders include difficulty falling asleep at a conventional bedtime, excessive daytime sleepiness, waking up too early or too late, fragmented and non-restorative sleep, irritability, mood disturbances, decreased concentration and cognitive function, and overall fatigue. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, productivity, and overall well-being. If you are experiencing persistent disruptions in your sleep patterns and daily rhythms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management of circadian rhythm disorder.