Sleep quality assessment is an essential tool for understanding how well we sleep and identifying potential issues that may be impacting our sleep. Poor sleep quality can lead to a range of health problems, including fatigue, mood disorders, and even chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. Therefore, it’s important to assess the quality of our sleep regularly.
There are several ways to assess sleep quality. One of the most common methods is through self-reporting using a questionnaire or survey. These assessments typically include questions about the duration of sleep, how long it takes to fall asleep, how often we wake up during the night, and how rested we feel upon waking up in the morning.
Another way to assess sleep quality is through objective measures such as polysomnography (PSG) or actigraphy. PSG involves monitoring brain waves, heart rate, breathing patterns, and muscle movements during sleep in a laboratory setting. Actigraphy involves wearing a device on your wrist that tracks movement during sleep and provides information about sleep patterns.
Regardless of the method used for assessing sleep quality, it’s important to consider several factors that can impact our ability to get a good night’s rest. These factors include lifestyle habits such as diet and exercise, stress levels, environmental factors such as noise and light pollution, and underlying medical conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea.
Assessing our sleep quality can help us identify potential areas for improvement in our sleeping habits. For example, if we consistently report feeling tired upon waking up in the morning despite getting an adequate amount of rest according to self-reporting or objective measures like actigraphy or PSGs; this could indicate an issue with our sleeping environment or lifestyle habits that may require adjustments.
In conclusion, assessing our sleep quality is an important step towards improving our overall health and well-being. By identifying potential issues with our sleeping habits early on through self-reporting or objective measures like PSGs or actigraphy; we can take steps to improve our sleep quality and reduce the risk of developing health problems associated with poor sleep.
Answers to 9 Common Questions About Assessing Sleep Quality
- What is the best way to assess sleep quality?
- How can I tell if my sleep quality is good or bad?
- What factors influence sleep quality?
- How do I improve my sleep quality?
- What are the signs of poor sleep quality?
- Are there any tests that measure sleep quality?
- How much sleep should I be getting for optimal health and wellbeing?
- Is there a difference between sleeping too much and sleeping too little?
- What are the benefits of good-quality sleep?
What is the best way to assess sleep quality?
The best way to assess sleep quality depends on the individual’s needs and preferences. There are various methods available, and each of them has its advantages and disadvantages.
Self-reporting using a questionnaire or survey is a commonly used method for assessing sleep quality. This method is easy to administer, cost-effective, and can be done at home. However, it relies on the individual’s ability to accurately recall their sleep patterns, which may not always be reliable.
Objective measures such as polysomnography (PSG) or actigraphy provide more detailed information about sleep patterns and can identify specific sleep disorders. PSG records brain waves, heart rate, breathing patterns, and muscle movements during sleep in a laboratory setting. Actigraphy involves wearing a device on your wrist that tracks movement during sleep and provides information about sleep patterns. These methods are more accurate than self-reporting but can be costly and require a visit to a sleep clinic.
Another way to assess sleep quality is by using mobile apps or wearable devices that track sleeping habits. These devices use sensors to monitor movement during the night and provide data on the duration of sleep, number of awakenings, and overall quality of sleep. This method is convenient as it can be done at home; however, the accuracy of these devices may vary.
In conclusion, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to assessing sleep quality. The best method depends on the individual’s needs and preferences. Self-reporting using a questionnaire or survey may be suitable for some individuals while others may require more detailed objective measures such as PSG or actigraphy. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your sleeping habits or suspect you have an underlying medical condition affecting your ability to get restful sleep.
How can I tell if my sleep quality is good or bad?
There are several signs that can indicate whether your sleep quality is good or bad. Here are some common indicators:
- You fall asleep within 15-20 minutes of going to bed: Falling asleep quickly is a sign that your body is tired and ready for rest.
- You stay asleep for most of the night: Waking up frequently during the night or having trouble falling back asleep can be a sign of poor sleep quality.
- You wake up feeling rested and refreshed: Feeling alert and energized upon waking up in the morning is a sign of good sleep quality.
- You don’t feel excessively sleepy during the day: If you find yourself nodding off during the day, it could be a sign that you’re not getting enough quality sleep at night.
- You don’t snore loudly or gasp for air during sleep: Snoring loudly or gasping for air while sleeping can be a sign of obstructive sleep apnea, which can disrupt your sleep and lead to health problems if left untreated.
- Your partner doesn’t report any disruptive sleeping habits: If your partner reports that you snore loudly, toss and turn frequently, or have other disruptive sleeping habits, it could be a sign that your sleep quality is poor.
If you’re experiencing any of these signs, it’s important to take steps to improve your sleep quality. This may include making changes to your sleeping environment, developing better bedtime habits, or seeking medical treatment if necessary. By improving your sleep quality, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
What factors influence sleep quality?
Several factors can impact sleep quality, including:
- Lifestyle habits: Our daily habits, such as diet and exercise, can affect sleep quality. Consuming caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime, for instance, can interfere with our ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Stress levels: High levels of stress can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Stress management techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises can help alleviate stress and improve sleep quality.
- Environmental factors: Noise, light pollution, temperature, and comfort level of the bed and pillows can all impact our ability to get a good night’s rest.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to poor sleep quality.
- Mental health issues: Anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues can interfere with our ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Age: As we age, our bodies produce less melatonin which is a hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles. This can lead to changes in sleeping patterns that may affect the quality of our sleep.
- Medications: Certain medications such as antidepressants or stimulants may interfere with our ability to fall asleep or stay asleep.
It’s essential to identify the factors that may be impacting your sleep quality so you can take steps towards improving your sleeping habits. This may include making lifestyle changes like reducing caffeine intake or practicing relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation. In some cases, seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional may be necessary to address underlying medical conditions that are affecting your sleep quality.
How do I improve my sleep quality?
Improving your sleep quality is essential for maintaining good physical and mental health. Here are some tips that can help you improve your sleep quality:
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Establish a bedtime routine that helps you relax before going to bed. This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
- Make your bedroom conducive to sleep: Ensure that your bedroom is cool, quiet, and dark. Use comfortable bedding and pillows that support your sleeping position.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine: These substances can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Limit screen time before bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices such as smartphones and tablets can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve the quality of your sleep. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime as it can make it difficult for you to fall asleep.
- Manage stress: Stress is one of the leading causes of poor sleep quality. Practice stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation or deep breathing exercises before going to bed.
- Consult with a healthcare professional: If you continue to experience poor sleep quality despite making lifestyle changes; consider consulting with a healthcare professional who can diagnose underlying medical conditions like obstructive sleep apnea or insomnia that may be impacting your ability to get good rest.
In summary, improving your sleep quality requires adopting healthy habits like sticking to a regular sleep schedule; creating a relaxing bedtime routine; making sure your bedroom is conducive to sleep; avoiding caffeine, alcohol and nicotine before bedtime; limiting screen time before bed; exercising regularly; managing stress effectively; and seeking professional advice if necessary.
What are the signs of poor sleep quality?
Poor sleep quality can manifest in several ways, and the signs can vary from person to person. However, there are some common signs that may indicate that you’re not getting enough restful sleep or that your sleep quality is poor. Here are some of the most common signs of poor sleep quality:
- Fatigue and daytime sleepiness: Feeling tired and sleepy during the day, even after getting what you think is enough sleep at night.
- Difficulty falling asleep: Struggling to fall asleep within 15-20 minutes of going to bed.
- Frequent waking up during the night: Waking up multiple times during the night and having trouble falling back to sleep.
- Snoring: Loud snoring or breathing interruptions during sleep may indicate a condition called obstructive sleep apnea, which can affect the quality of your sleep.
- Restless leg syndrome: Unpleasant sensations in the legs that cause an irresistible urge to move them, often leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Morning headaches: Waking up with a headache can be a sign of poor-quality sleep or an underlying medical condition such as sleep apnea.
- Mood changes: Poor-quality sleep can cause irritability, mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
- Lack of concentration and memory problems: Difficulty concentrating during the day and remembering things may be a sign that you’re not getting enough restful sleep at night.
If you’re experiencing any of these signs regularly, it’s essential to assess your sleeping habits and make changes if necessary. Improving your sleeping habits can have significant benefits for your overall health and well-being.
Are there any tests that measure sleep quality?
Yes, there are several tests that measure sleep quality. Some of the most common tests include:
- Polysomnography (PSG): This is a comprehensive test that measures brain waves, eye movements, heart rate, breathing patterns, and muscle movements during sleep. PSG is often conducted in a sleep lab and can provide detailed information about sleep quality.
- Actigraphy: This test involves wearing a small device on the wrist that measures movement during sleep. Actigraphy can provide information about the duration and quality of sleep.
- Sleep diary: A sleep diary is a self-reported record of sleeping habits and patterns over a period of time. It typically includes information about when you go to bed, how long it takes to fall asleep, how often you wake up during the night, and how rested you feel upon waking up in the morning.
- Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS): This is a questionnaire that assesses daytime sleepiness by asking questions about how likely you are to fall asleep in different situations.
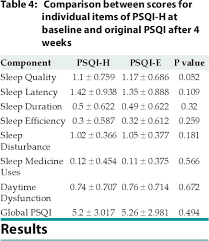
- Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI): This questionnaire assesses overall sleep quality by asking questions about factors such as sleep duration, latency (time it takes to fall asleep), efficiency (percentage of time spent sleeping while in bed), disturbances (how often you wake up during the night), and daytime dysfunction (how much your sleep problems affect your daily functioning).
These tests can help identify potential issues with sleeping habits or underlying medical conditions that may be affecting sleep quality. If you are experiencing persistent problems with sleeping or feel excessively tired during the day despite getting enough rest at night, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider who may recommend one or more of these tests to evaluate your sleep quality.
How much sleep should I be getting for optimal health and wellbeing?
The amount of sleep required for optimal health and wellbeing varies depending on several factors such as age, lifestyle, and individual needs. However, the National Sleep Foundation recommends the following guidelines for adults:
– Adults aged 18-64: 7-9 hours of sleep per night
– Adults aged 65 and older: 7-8 hours of sleep per night
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and some individuals may require more or less sleep than others. Factors such as stress levels, physical activity levels, medical conditions, and medication use can all impact our sleep needs.
Getting enough sleep is crucial for maintaining good health and wellbeing. Consistently getting less than the recommended amount of sleep has been linked to a range of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
In addition to getting enough sleep each night, it’s also important to prioritize good sleep hygiene practices such as creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, keeping a consistent sleep schedule even on weekends, and creating a comfortable sleeping environment.
If you’re consistently having trouble getting enough restful sleep despite making changes to your sleeping habits or experiencing symptoms such as excessive daytime fatigue or snoring; it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider who can help identify potential underlying causes for your sleep issues.
Is there a difference between sleeping too much and sleeping too little?
Yes, there is a difference between sleeping too much and sleeping too little. While both can have negative effects on our health, the specific consequences of each can differ.
Sleeping too little, also known as sleep deprivation, can lead to a range of issues such as fatigue, decreased concentration and productivity, mood changes, and an increased risk of accidents. Chronic sleep deprivation has also been linked to long-term health problems such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and depression.
On the other hand, sleeping too much can also have negative effects on our health. Oversleeping has been associated with an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. It can also lead to feelings of grogginess or lethargy throughout the day.
In addition to the physical health consequences of oversleeping or sleep deprivation; there are also mental health implications. Sleeping too little has been linked to an increased risk of anxiety and depression while oversleeping has been associated with symptoms of depression.
It’s important to note that the optimal amount of sleep varies from person to person and depends on factors such as age and lifestyle habits. While most adults require between 7-9 hours of sleep per night; some individuals may need more or less depending on their individual needs.
In conclusion; while both sleeping too much and sleeping too little can have negative effects on our health; the specific consequences may differ. It’s important to strive for a healthy balance in our sleep habits by aiming for the optimal amount of rest based on our individual needs.
What are the benefits of good-quality sleep?
Getting good-quality sleep is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. Here are some of the benefits of getting a good night’s sleep:
- Improved Mood: Good-quality sleep can help improve our mood and reduce the risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Increased Energy: Quality sleep can help us feel more rested and energized throughout the day, improving our productivity and overall quality of life.
- Better Memory: Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, helping us remember important information and improve our learning abilities.
- Reduced Inflammation: Poor sleep quality has been linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can increase the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Improved Immune Function: Sleep plays a vital role in strengthening our immune system, helping us fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
- Weight Management: Lack of sleep has been linked to weight gain and obesity, while good-quality sleep can help regulate appetite hormones and promote healthy weight management.
- Reduced Risk of Accidents: Good-quality sleep can help reduce the risk of accidents caused by fatigue, such as car accidents or workplace injuries.
In summary, getting good-quality sleep is crucial for maintaining good health and well-being. It can improve our mood, increase energy levels, boost memory retention, reduce inflammation in the body, strengthen immune function, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of accidents caused by fatigue.