The Complex Nature of Bipolar 1 Disorder
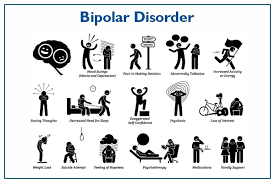
Bipolar 1 disorder is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that include manic episodes and depressive episodes. It is considered a complex and challenging disorder to manage, as individuals with bipolar 1 may experience intense emotional highs and lows that can significantly impact their daily lives.
Manic Episodes
During manic episodes, individuals with bipolar 1 may feel euphoric, energetic, and overly confident. They may engage in risky behaviors, have racing thoughts, and exhibit impulsive decision-making. While some may view manic episodes as periods of heightened creativity and productivity, they can also lead to reckless behavior and strained relationships.
Depressive Episodes
In contrast, depressive episodes in bipolar 1 disorder are characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. Individuals may struggle with low energy levels, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide. These depressive episodes can be debilitating and require professional intervention.
Treatment Options
Managing bipolar 1 disorder typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Mood stabilizers are commonly prescribed to help regulate mood swings, while therapy sessions can provide coping strategies and emotional support. Additionally, maintaining a healthy routine that includes regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can help individuals better manage their symptoms.
Supporting Individuals with Bipolar 1 Disorder
It is essential for family members, friends, and healthcare providers to offer understanding and support to individuals living with bipolar 1 disorder. Educating oneself about the condition, practicing empathy, encouraging treatment adherence, and fostering open communication can all contribute to creating a supportive environment for those managing this challenging mental health condition.
In Conclusion
Bipolar 1 disorder is a complex mental health condition that requires comprehensive treatment and ongoing support. By raising awareness about the symptoms and challenges associated with bipolar 1 disorder, we can work towards reducing stigma and promoting effective management strategies for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Bipolar 1: Answers to Common Questions
- What is difference between bipolar 1 and 2?
- What is the difference between bipolar 1 and 2?
- Is bipolar 1 a serious mental illness?
- What does having bipolar 1 mean?
- What is a bipolar type 1 behavior?
- Can people with bipolar 1 live a normal life?
- What is a person with bipolar 1 like?
- What does bipolar 1 do to the brain?
What is difference between bipolar 1 and 2?
Bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 are two distinct subtypes of bipolar disorder, each characterized by varying degrees of mood episodes. The primary difference between the two lies in the severity of manic episodes experienced. Bipolar 1 disorder involves manic episodes that can be severe and may require immediate medical attention, while depressive episodes may also occur. On the other hand, bipolar 2 disorder is characterized by less intense manic episodes, known as hypomanic episodes, along with depressive episodes. It is essential to consult a mental health professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
What is the difference between bipolar 1 and 2?
Bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 are two distinct subtypes of bipolar disorder, each characterized by unique features. The primary difference between bipolar 1 and bipolar 2 lies in the severity of manic episodes experienced by individuals. In bipolar 1 disorder, individuals experience full-blown manic episodes that can be intense and disruptive, often requiring immediate medical attention. On the other hand, bipolar 2 disorder is characterized by less severe manic episodes known as hypomania, which may not cause significant impairment in daily functioning. Additionally, individuals with bipolar 2 experience more prominent depressive episodes compared to those with bipolar 1. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning for individuals living with either subtype of bipolar disorder.
Is bipolar 1 a serious mental illness?
Bipolar 1 disorder is indeed considered a serious mental illness due to its significant impact on an individual’s life and well-being. The extreme mood swings characteristic of bipolar 1, including manic episodes of heightened energy and depressive episodes of profound sadness, can disrupt daily functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life. Without proper diagnosis and management, bipolar 1 can lead to severe consequences such as impaired decision-making, risky behaviors, challenges in maintaining employment or academic performance, and an increased risk of self-harm or suicide. It is crucial for individuals with bipolar 1 to receive timely and comprehensive treatment from healthcare professionals to effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall mental health outcomes.
What does having bipolar 1 mean?
Having bipolar 1 means experiencing extreme mood swings characterized by manic episodes and depressive episodes. Individuals with bipolar 1 disorder may go through periods of intense euphoria, high energy levels, and impulsive behavior during manic episodes, followed by phases of profound sadness, fatigue, and loss of interest in depressive episodes. This mental health condition can significantly impact daily functioning and relationships, requiring a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments for effective management. Understanding the complexities of bipolar 1 disorder is crucial in providing support and resources to those navigating its challenges.
What is a bipolar type 1 behavior?
Bipolar type 1 behavior refers to the characteristic mood fluctuations exhibited by individuals diagnosed with bipolar 1 disorder. These behaviors typically include extreme shifts between manic episodes, marked by elevated mood, increased energy, and impulsivity, and depressive episodes, characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low energy. Individuals with bipolar 1 may display erratic behavior during manic phases, such as engaging in risky activities or making impulsive decisions. Understanding these distinct behavioral patterns is crucial in diagnosing and effectively managing bipolar 1 disorder to help individuals navigate their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Can people with bipolar 1 live a normal life?
For individuals with bipolar 1 disorder, the question of whether they can live a normal life is a common concern. While bipolar 1 disorder presents unique challenges due to its fluctuating mood states, with proper treatment and support, many individuals can lead fulfilling and productive lives. By adhering to a treatment plan that may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with bipolar 1 can effectively manage their symptoms and reduce the impact of manic and depressive episodes on their daily functioning. Additionally, having a strong support system, open communication with healthcare providers, and self-awareness about triggers and warning signs can empower individuals with bipolar 1 to navigate their condition successfully and work towards achieving stability in various aspects of their lives.
What is a person with bipolar 1 like?
A person with bipolar 1 disorder experiences extreme mood swings that manifest as manic episodes and depressive episodes. During manic episodes, they may exhibit heightened energy, impulsivity, and euphoria, often engaging in risky behaviors. On the other hand, depressive episodes are characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low energy levels. Individuals with bipolar 1 disorder may struggle to regulate their emotions and behavior, impacting their daily functioning and relationships. It is important to understand that each person’s experience with bipolar 1 disorder is unique, and treatment tailored to their specific needs is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
What does bipolar 1 do to the brain?
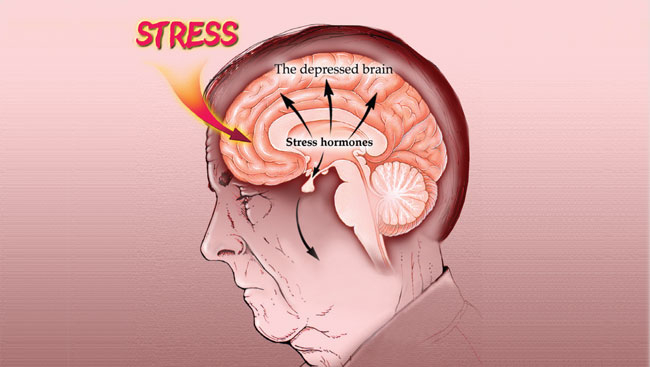
Bipolar 1 disorder affects the brain by disrupting the normal balance of neurotransmitters, chemicals that transmit signals between brain cells. During manic episodes, there is an increase in dopamine and norepinephrine levels, leading to heightened arousal and energy. Conversely, depressive episodes are associated with decreased levels of these neurotransmitters, resulting in feelings of sadness and lethargy. These fluctuations in neurotransmitter levels can impact mood regulation, cognitive function, and emotional processing in individuals with bipolar 1 disorder. Additionally, structural changes in certain brain regions have been observed in individuals with bipolar disorder, highlighting the complex interplay between biological factors and mental health symptoms.