The Link Between Depression and Insomnia
Depression and insomnia are two common mental health issues that often go hand in hand. While they are distinct conditions, they can frequently coexist and exacerbate each other, creating a challenging cycle that impacts a person’s overall well-being.
Understanding Depression
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. It can affect how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, leading to various emotional and physical symptoms.
Exploring Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it difficult for individuals to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. People with insomnia often experience fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and other daytime impairments due to insufficient or poor-quality sleep.
The Relationship Between Depression and Insomnia
Research suggests a bidirectional relationship between depression and insomnia. Individuals with depression are more likely to experience sleep disturbances, such as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Conversely, chronic insomnia can increase the risk of developing depression or worsening existing depressive symptoms.
Treating Depression and Insomnia Together
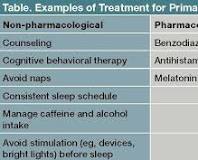
Addressing both depression and insomnia simultaneously is crucial for effective treatment outcomes. Therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can help improve sleep patterns while also targeting underlying depressive symptoms. Additionally, medication management and lifestyle modifications may be recommended to address both conditions comprehensively.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are experiencing symptoms of depression or insomnia, it is essential to seek support from healthcare professionals. A mental health provider can conduct an evaluation to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
By recognizing the link between depression and insomnia and taking proactive steps to address both conditions, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and quality of life.
Understanding the Link: Depression and Insomnia FAQs
- What is the relationship between depression and insomnia?
- How does insomnia contribute to or worsen depression?
- What are common symptoms of both depression and insomnia?
- What treatment options are available for individuals with coexisting depression and insomnia?
- Are there lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms of both depression and insomnia?
What is the relationship between depression and insomnia?
The relationship between depression and insomnia is complex and interconnected. Individuals with depression often experience disruptions in their sleep patterns, such as difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. Conversely, chronic insomnia can contribute to the development or exacerbation of depressive symptoms. The bidirectional nature of this relationship highlights how one condition can influence and perpetuate the other, creating a challenging cycle that impacts an individual’s mental health and overall well-being. Recognizing and addressing both depression and insomnia together is essential for comprehensive treatment and improved outcomes.
How does insomnia contribute to or worsen depression?
Insomnia can significantly contribute to or exacerbate depression by disrupting the delicate balance of mental and emotional well-being. When individuals experience chronic sleep difficulties, such as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, it can lead to a range of negative consequences. Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive function, emotional regulation, and stress management, making individuals more vulnerable to developing or worsening depressive symptoms. The persistent exhaustion and irritability resulting from insomnia can further impact mood and overall mental health, creating a cycle where sleep disturbances fuel depressive tendencies and vice versa. Addressing insomnia is crucial in managing depression effectively, as improving sleep quality can help alleviate some of the burdens on mental health and enhance overall emotional resilience.
What are common symptoms of both depression and insomnia?
Common symptoms of both depression and insomnia often overlap, contributing to the complex relationship between these two conditions. In individuals experiencing depression, common symptoms include persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite or weight, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide. Similarly, insomnia manifests through difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep throughout the night, waking up too early and being unable to go back to sleep, daytime fatigue or sleepiness, irritability, and impaired concentration or memory. Recognizing these shared symptoms is crucial in identifying the interconnectedness of depression and insomnia and seeking appropriate treatment to address both mental health concerns effectively.
What treatment options are available for individuals with coexisting depression and insomnia?
For individuals grappling with the challenging dual burden of depression and insomnia, various treatment options are available to address both conditions concurrently. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is a widely recognized approach that targets sleep disturbances while also addressing underlying depressive symptoms. Additionally, healthcare providers may recommend a combination of therapy, medication management, and lifestyle modifications to effectively manage both depression and insomnia. Seeking professional help is crucial to receive personalized care and guidance tailored to the individual’s unique needs, ultimately promoting better sleep quality and mental well-being.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms of both depression and insomnia?
Making lifestyle changes can be instrumental in alleviating symptoms of both depression and insomnia. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and establishing a consistent sleep routine are essential practices that can positively impact mental health and sleep quality. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation, contributing to improved mood and better sleep. Limiting the consumption of stimulants like caffeine and alcohol, especially close to bedtime, can also support healthier sleep patterns. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals may experience relief from symptoms of depression and insomnia while enhancing their overall well-being.