Sleep Apnea and Insomnia: Understanding the Differences
Sleep apnea and insomnia are two common sleep disorders that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While both conditions can lead to sleep disturbances, they have distinct causes and symptoms.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common form of sleep apnea and occurs when the muscles in the throat relax, causing the airway to become blocked.
- Central Sleep Apnea: In this type, the brain fails to send signals to the muscles that control breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: This is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Common symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, daytime fatigue, morning headaches, and irritability. If left untreated, sleep apnea can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a condition characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term) and may be caused by various factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, or poor sleep habits.
Common symptoms of insomnia include difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently during the night, waking up too early in the morning, and feeling tired upon waking. Insomnia can have a significant impact on daily functioning, mood, and overall well-being.
Differences Between Sleep Apnea and Insomnia
The key differences between sleep apnea and insomnia lie in their causes and symptoms:
- Cause: Sleep apnea is primarily caused by physical obstructions in the airway or neurological issues affecting breathing patterns. On the other hand, insomnia is often linked to psychological factors such as stress or anxiety.
- Symptoms: While both conditions can lead to poor quality sleep and daytime fatigue, individuals with sleep apnea may experience pauses in breathing during sleep (apneas), while those with insomnia struggle more with falling asleep or staying asleep.
If you suspect that you may have either sleep apnea or insomnia, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options. Both conditions can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes, therapy, or medical interventions tailored to individual needs.
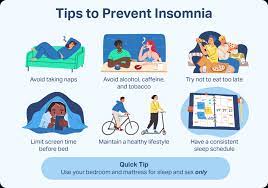
7 Effective Tips to Combat Sleep Apnea and Insomnia for a Restful Night
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of sleep apnea.
- Avoid sleeping on your back to help prevent airway blockage during sleep.
- Limit alcohol and sedative intake as they can worsen symptoms of sleep apnea.
- Consider elevating your head while sleeping to help keep airways open.
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine to signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
- Create a comfortable sleep environment that is conducive to relaxation and restful sleep.
- Try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to calm the mind before bed.
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of sleep apnea.
Maintaining a healthy weight is a crucial tip to reduce the risk of sleep apnea. Excess weight can contribute to the narrowing of the airways, leading to breathing difficulties during sleep. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet, individuals can not only manage their weight but also improve their overall sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of developing sleep apnea. Prioritizing weight management as part of a comprehensive approach to health can have significant benefits in promoting better sleep and overall well-being.
Avoid sleeping on your back to help prevent airway blockage during sleep.
To help prevent airway blockage during sleep and reduce the risk of sleep apnea or worsening insomnia, it is advisable to avoid sleeping on your back. When you sleep on your back, gravity can cause the tongue and soft tissues in the throat to collapse backward, potentially obstructing the airway and leading to breathing difficulties. By sleeping on your side or in a slightly elevated position, you can promote better airflow and minimize the likelihood of experiencing interruptions in breathing during the night. Making this simple adjustment to your sleeping position may contribute to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
Limit alcohol and sedative intake as they can worsen symptoms of sleep apnea.
Limiting alcohol and sedative intake is crucial for individuals with sleep apnea as these substances can exacerbate symptoms of the condition. Alcohol and sedatives have a relaxing effect on the muscles in the throat, which can lead to increased airway obstruction during sleep, making breathing more difficult. By reducing or avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, individuals with sleep apnea can improve their quality of sleep and reduce the severity of their symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing sleep apnea effectively.
Consider elevating your head while sleeping to help keep airways open.
Elevating your head while sleeping can be a helpful tip for individuals dealing with sleep apnea or insomnia. By keeping your head slightly elevated, gravity can assist in preventing the collapse of the airway during sleep, reducing the likelihood of breathing interruptions associated with sleep apnea. Additionally, this position can help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux and congestion, promoting better airflow and more restful sleep for those struggling with insomnia. Making simple adjustments like using a wedge pillow or raising the head of your bed may contribute to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
Establish a consistent bedtime routine to signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can be a helpful strategy to signal your body that it’s time to wind down, especially for individuals dealing with sleep apnea or insomnia. By following a regular sequence of calming activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques, you can create a sense of predictability and relaxation that cues your body to prepare for sleep. This routine can help regulate your internal clock and promote better sleep quality over time.
Create a comfortable sleep environment that is conducive to relaxation and restful sleep.
Creating a comfortable sleep environment that promotes relaxation and restful sleep is essential for managing sleep apnea and insomnia. By setting up a conducive space free of distractions, noise, and excessive light, you can signal to your body that it’s time to unwind and prepare for rest. Consider factors such as comfortable bedding, optimal room temperature, and calming bedtime routines to help improve the quality of your sleep and alleviate symptoms associated with these sleep disorders.
Try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to calm the mind before bed.
To improve sleep quality and manage symptoms of sleep apnea and insomnia, it is beneficial to incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation into your bedtime routine. These practices can help calm the mind, reduce stress and anxiety, and promote a sense of relaxation that prepares the body for restful sleep. By engaging in deep breathing exercises or meditation before bed, you can create a peaceful environment conducive to falling asleep easily and experiencing a more restorative night’s rest.