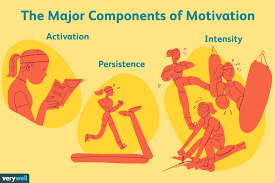
The Psychology of Motivation: Understanding What Drives Us
Motivation is a complex psychological concept that plays a crucial role in driving human behavior. It is the inner force that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented actions. Understanding the psychology behind motivation can help us unlock our full potential and achieve our goals.
Types of Motivation
Psychologists have identified two main types of motivation: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation comes from within and is driven by internal rewards such as personal satisfaction, enjoyment, or a sense of accomplishment. Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, comes from external factors like rewards, recognition, or punishment.
Theories of Motivation
Several theories have been proposed to explain what motivates us. One prominent theory is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which suggests that individuals are motivated to fulfill basic needs such as food, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization in a hierarchical order.
Another influential theory is Self-Determination Theory (SDT), which posits that humans have three basic psychological needs: autonomy (feeling in control), competence (feeling capable), and relatedness (feeling connected to others). When these needs are met, individuals are more likely to be motivated intrinsically.
Factors Influencing Motivation
Various factors can influence our motivation levels. These include:
- Goals: Clear and achievable goals can boost motivation by providing a sense of direction and purpose.
- Rewards: Positive reinforcement through rewards can increase motivation levels for certain tasks or behaviors.
- Beliefs: Our beliefs about our abilities (self-efficacy) and the importance of a task can impact our motivation to pursue it.
- Social Factors: Social support, encouragement, and competition can influence our motivation levels.
The Role of Emotions in Motivation
Emotions play a significant role in motivating behavior. Positive emotions like joy and excitement can enhance motivation by making tasks more enjoyable and rewarding. Conversely, negative emotions like fear or anxiety can hinder motivation by creating barriers to action.
Cultivating Motivation
To cultivate and maintain motivation, it’s essential to:
- Set Clear Goals: Define specific, measurable goals that align with your values and aspirations.
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge your achievements along the way to stay motivated and focused.
- Foster Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself during setbacks or challenges to maintain intrinsic motivation.
- Create a Supportive Environment: Surround yourself with positive influences that encourage and inspire you.
In conclusion, understanding the psychology of motivation empowers us to harness our inner drive effectively. By recognizing the factors influencing our motivation levels and adopting strategies to cultivate it, we can propel ourselves toward success in various aspects of life.
Exploring Motivation Psychology: Key Questions and Insights
- What is motivation psychology?
- Why is motivation important in psychology?
- What are the different types of motivation according to psychology?
- How does intrinsic motivation differ from extrinsic motivation?
- What are some popular theories of motivation in psychology?
- How do basic psychological needs influence motivation?
- What factors can affect an individual’s level of motivation?
- How do emotions play a role in motivating behavior according to psychology?
- What strategies can be used to enhance and maintain motivation?
What is motivation psychology?
Motivation psychology is the branch of psychology that focuses on understanding the factors that drive and influence human behavior. It delves into the underlying reasons why individuals initiate, sustain, and direct their actions toward specific goals or outcomes. By exploring concepts such as intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, theories like Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, and the role of emotions in shaping motivation, motivation psychology seeks to unravel the complexities of what motivates us as individuals. This field of study not only sheds light on the various factors influencing our drive and determination but also provides valuable insights into how we can enhance our motivation levels to achieve personal and professional success.
Why is motivation important in psychology?
Motivation plays a crucial role in psychology as it serves as the driving force behind human behavior and actions. Understanding motivation is essential for psychologists as it helps explain why individuals initiate, sustain, and direct their efforts towards specific goals or tasks. By studying motivation, psychologists can gain insights into how intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence behavior, decision-making, and overall well-being. Additionally, motivation is closely linked to various psychological processes such as learning, emotion regulation, and self-regulation. Ultimately, recognizing the importance of motivation in psychology allows professionals to develop effective strategies for enhancing motivation levels, promoting personal growth, and achieving positive outcomes in individuals’ lives.
What are the different types of motivation according to psychology?
In the realm of psychology, there are two primary types of motivation: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation stems from internal drives and rewards, such as personal satisfaction, enjoyment, or a sense of accomplishment. On the other hand, extrinsic motivation is fueled by external factors like rewards, recognition, or avoidance of punishment. Understanding these distinct types of motivation is crucial in comprehending what drives individuals to pursue their goals and engage in specific behaviors. By recognizing the interplay between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, psychologists can provide valuable insights into how to effectively motivate individuals in various contexts.
How does intrinsic motivation differ from extrinsic motivation?
Intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation are two distinct forms of drive that influence human behavior. Intrinsic motivation stems from internal factors, such as personal enjoyment, satisfaction, or a sense of fulfillment derived from the activity itself. Individuals driven by intrinsic motivation engage in tasks because they find them inherently rewarding or meaningful. On the other hand, extrinsic motivation is fueled by external factors like rewards, recognition, or punishments. People motivated extrinsically perform tasks to attain a specific outcome or avoid negative consequences rather than for the inherent enjoyment of the activity. Understanding the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation is crucial in designing effective strategies to enhance engagement and productivity in various contexts.
What are some popular theories of motivation in psychology?
In the field of psychology, several popular theories of motivation have been proposed to explain what drives human behavior. One widely recognized theory is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which suggests that individuals are motivated to fulfill a hierarchy of basic needs, progressing from physiological needs to self-actualization. Another influential theory is Self-Determination Theory (SDT), which emphasizes the importance of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in fostering intrinsic motivation. Additionally, Expectancy Theory posits that individuals are motivated by their beliefs about the relationship between effort, performance, and outcomes. These theories offer valuable insights into the complex mechanisms underlying human motivation and provide a framework for understanding and enhancing motivational processes.
How do basic psychological needs influence motivation?
Basic psychological needs play a fundamental role in influencing motivation according to Self-Determination Theory. These needs, including autonomy, competence, and relatedness, serve as essential drivers of human behavior and motivation. Autonomy refers to the need for individuals to feel in control of their actions and decisions, which can enhance intrinsic motivation. Competence reflects the desire to feel capable and effective in one’s pursuits, leading to increased motivation to master tasks. Relatedness involves the need for social connection and belonging, which can boost motivation through support and collaboration with others. When these basic psychological needs are met, individuals are more likely to experience a sense of fulfillment, engagement, and sustained motivation in pursuing their goals.
What factors can affect an individual’s level of motivation?
Various factors can influence an individual’s level of motivation. These include the clarity and attainability of goals set by the individual, the presence of rewards or positive reinforcement for desired behaviors, the individual’s beliefs in their own capabilities (self-efficacy), as well as external social factors such as support from others or competitive environments. Additionally, emotions play a significant role in shaping motivation, with positive emotions enhancing motivation and negative emotions potentially hindering it. Creating a supportive environment that fosters intrinsic motivation and setting clear, meaningful goals are crucial in maintaining and boosting an individual’s motivation levels.
How do emotions play a role in motivating behavior according to psychology?
Emotions play a crucial role in motivating behavior according to psychology. Positive emotions such as joy, excitement, and passion can enhance motivation by making tasks more enjoyable and rewarding. When individuals experience positive emotions in relation to a particular goal or activity, they are more likely to be driven to pursue it with enthusiasm and dedication. On the other hand, negative emotions like fear, anxiety, or frustration can act as barriers to motivation by creating mental roadblocks and hindering progress. Understanding how emotions influence motivation is essential in shaping behaviors and achieving desired outcomes in various aspects of life.
What strategies can be used to enhance and maintain motivation?
To enhance and maintain motivation, various strategies can be employed to keep individuals engaged and driven towards their goals. Setting clear and achievable goals is essential, as it provides a sense of direction and purpose. Celebrating progress along the way can boost motivation by acknowledging achievements and milestones reached. Fostering self-compassion during setbacks or challenges is crucial to maintaining intrinsic motivation. Creating a supportive environment with positive influences that encourage and inspire can also help sustain motivation levels. By implementing these strategies consistently, individuals can enhance their motivation and stay focused on their objectives.