Understanding PTSD Insomnia
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing a traumatic event. One common symptom of PTSD is insomnia, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and overall well-being.
Individuals with PTSD often experience recurring nightmares, flashbacks, and intrusive thoughts related to the traumatic event. These symptoms can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to chronic insomnia.
PTSD-related insomnia can have various effects on physical and mental health. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate existing PTSD symptoms, such as anxiety and irritability, making it challenging for individuals to cope with daily stressors.
Furthermore, the cycle of poor sleep quality can contribute to a worsening of overall mental health, including increased risk of depression and other mood disorders. It can also impact cognitive function, memory retention, and decision-making abilities.
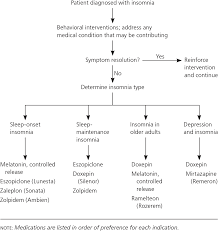
Managing PTSD-related insomnia requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying trauma and the sleep disturbances. Treatment options may include therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia), medication, relaxation techniques, and creating a conducive sleep environment.
It is essential for individuals with PTSD to seek professional help from mental health professionals who specialize in trauma-related disorders. By addressing both the trauma and sleep issues simultaneously, individuals can work towards improving their overall well-being and quality of life.
If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD-related insomnia, remember that help is available. Reach out to a healthcare provider or therapist to explore treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding PTSD and Insomnia: Common Questions Answered
- Can you get insomnia from PTSD?
- How do I stop PTSD insomnia?
- What are the four types of PTSD?
- Can PTSD cause insomnia?
- What does a PTSD episode look like?
- What are the 17 symptoms of complex PTSD?
Can you get insomnia from PTSD?
Yes, insomnia is a common symptom that can result from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Individuals with PTSD often experience difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep due to the recurring nightmares, flashbacks, and intrusive thoughts associated with the traumatic event. The hyperarousal and heightened anxiety levels characteristic of PTSD can disrupt the normal sleep-wake cycle, leading to chronic insomnia. Addressing both the underlying trauma and the sleep disturbances is crucial in managing PTSD-related insomnia effectively. Seeking professional help from mental health professionals who specialize in trauma-related disorders can provide guidance on treatment options tailored to alleviate both the trauma symptoms and sleep difficulties.
How do I stop PTSD insomnia?
To address PTSD insomnia, it is crucial to adopt a comprehensive approach that combines strategies to manage both the underlying trauma of PTSD and the sleep disturbances. Seeking professional help from mental health professionals who specialize in trauma-related disorders is essential. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), medication, relaxation techniques, and creating a sleep-conducive environment are common approaches used to alleviate PTSD-related insomnia. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and promotes better sleep quality and overall well-being.
What are the four types of PTSD?
There are four main types of PTSD, each characterized by distinct symptoms and manifestations: 1) Intrusive memories, such as flashbacks or nightmares related to the traumatic event; 2) Avoidance behaviors, where individuals may try to avoid people, places, or activities that remind them of the trauma; 3) Negative changes in mood and thinking, including feelings of guilt, shame, or detachment from others; and 4) Changes in physical and emotional reactions, such as heightened anxiety, irritability, or being easily startled. Understanding these different types of PTSD can help individuals recognize their symptoms and seek appropriate support and treatment.
Can PTSD cause insomnia?
Yes, PTSD can indeed cause insomnia. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia. Individuals with PTSD often experience intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and heightened anxiety related to the traumatic event they have experienced. These symptoms can make it challenging to fall asleep or stay asleep, resulting in sleep disturbances and chronic insomnia. Addressing the underlying trauma through therapy and developing healthy sleep habits are crucial steps in managing PTSD-related insomnia and improving overall well-being.
What does a PTSD episode look like?
A PTSD episode can manifest in various ways, depending on the individual and the nature of their trauma. During a PTSD episode, a person may experience intense feelings of fear, anxiety, or distress triggered by reminders of the traumatic event. This can lead to symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, hypervigilance, irritability, and avoidance behaviors. Physiological responses like increased heart rate, sweating, and trembling may also occur. The individual may feel overwhelmed by emotions and have difficulty concentrating or engaging in daily activities. It’s important to recognize these signs and seek appropriate support and treatment to manage PTSD episodes effectively.
What are the 17 symptoms of complex PTSD?
Complex PTSD, also known as C-PTSD, is a condition that can develop in individuals who have experienced prolonged and repeated trauma, often in interpersonal relationships or captivity. The 17 symptoms of complex PTSD may include but are not limited to: emotional dysregulation, persistent feelings of shame or guilt, difficulty trusting others, self-destructive behavior, dissociation, chronic feelings of emptiness or hopelessness, difficulty managing emotions, and a distorted self-perception. Other symptoms may involve difficulties with relationships, negative self-perception, and a heightened sense of isolation and loneliness. It is important for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek professional help from mental health experts who can provide appropriate support and treatment tailored to their specific needs.