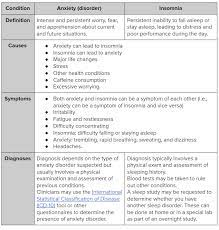
The Connection Between PTSD and Insomnia
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing a traumatic event. Individuals with PTSD often experience a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, and hypervigilance. One common yet often overlooked symptom of PTSD is insomnia.
Understanding the Link
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. For individuals with PTSD, insomnia can be a debilitating symptom that exacerbates other aspects of their condition. The link between PTSD and insomnia is complex and multifaceted.
Biological Factors
Research suggests that individuals with PTSD may have alterations in their brain chemistry that contribute to sleep disturbances. The stress response system in the body, including the release of cortisol and adrenaline, can impact sleep patterns and make it difficult for individuals to relax and fall asleep.
Psychological Factors
The intrusive thoughts and memories associated with PTSD can be particularly disruptive at night, leading to nightmares and disturbed sleep. Individuals may also experience hyperarousal symptoms that make it challenging to wind down before bedtime.
The Impact on Overall Well-Being
Chronic insomnia not only affects quality of life but can also worsen existing symptoms of PTSD. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased irritability, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, and impaired cognitive function. Over time, this can further exacerbate feelings of distress and anxiety associated with PTSD.
Treatment Approaches
Addressing both PTSD and insomnia is crucial for improving overall well-being. Treatment approaches may include therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia), medication management, relaxation techniques, mindfulness practices, and creating a conducive sleep environment.
Seeking Support
If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD-related insomnia, it’s essential to seek professional help. A mental health provider can assess your symptoms, develop a tailored treatment plan, and provide support throughout your recovery journey.
8 Effective Tips for Managing PTSD-Related Insomnia
- Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
- Limit screen time before bed as the blue light can disrupt your sleep patterns.
- Practice deep breathing or meditation techniques to calm your mind before sleep.
- Create a comfortable sleep environment with minimal distractions and noise.
- Avoid caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime as they can interfere with your sleep.
- Consider seeking therapy or counseling to address underlying PTSD symptoms affecting your sleep.
- Engage in regular physical activity during the day, but avoid intense exercise close to bedtime.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on potential medication options for managing PTSD-related insomnia.
Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine can be a helpful tip for individuals experiencing PTSD-related insomnia. By creating a consistent series of calming activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises, you can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This routine can help reduce anxiety and hyperarousal symptoms commonly associated with PTSD, promoting a sense of relaxation and improving the chances of falling asleep more easily.
Limit screen time before bed as the blue light can disrupt your sleep patterns.
Limiting screen time before bed is a helpful tip for individuals experiencing PTSD-related insomnia. The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. By reducing exposure to screens in the hours leading up to bedtime, individuals may find it easier to relax and prepare their mind and body for a restful night’s sleep. This simple adjustment can contribute to better sleep hygiene and potentially alleviate some of the sleep disturbances associated with PTSD.
Practice deep breathing or meditation techniques to calm your mind before sleep.
To alleviate the symptoms of PTSD-related insomnia, consider incorporating deep breathing or meditation techniques into your bedtime routine. By practicing these calming strategies before sleep, you can help quiet your mind, reduce anxiety, and promote relaxation. Deep breathing exercises and meditation can create a sense of inner peace, making it easier to transition into a restful state and improve the quality of your sleep.
Create a comfortable sleep environment with minimal distractions and noise.
Creating a comfortable sleep environment with minimal distractions and noise can be particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with PTSD-related insomnia. By eliminating external stimuli that may trigger heightened anxiety or intrusive thoughts, such as loud noises or excessive light, you can promote a sense of calm and relaxation conducive to better sleep. This simple tip can help create a peaceful sanctuary where you can unwind and improve your chances of getting the restorative sleep needed for overall well-being and mental health.
Avoid caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime as they can interfere with your sleep.
To manage symptoms of PTSD-related insomnia, it is advisable to avoid consuming caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and certain sodas, can disrupt sleep by stimulating the nervous system and increasing alertness. Similarly, heavy meals can lead to discomfort and indigestion, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. By steering clear of these sleep-disrupting substances and foods before bedtime, individuals with PTSD can create a more conducive environment for restful sleep and improved overall well-being.
Consider seeking therapy or counseling to address underlying PTSD symptoms affecting your sleep.
Consider seeking therapy or counseling to address underlying PTSD symptoms that may be impacting your sleep. Therapy can provide a safe and supportive space to explore and process traumatic experiences, develop coping strategies for managing symptoms, and learn relaxation techniques to improve sleep quality. A mental health professional can work with you to tailor a treatment plan that addresses both the PTSD symptoms and insomnia, helping you on your journey towards better sleep and overall well-being.
Engage in regular physical activity during the day, but avoid intense exercise close to bedtime.
Engaging in regular physical activity during the day can be beneficial for individuals dealing with PTSD-related insomnia. Exercise helps reduce stress, improve mood, and promote better sleep quality. However, it is important to avoid intense exercise close to bedtime as it can increase alertness and make it harder to wind down for sleep. Opting for gentle activities like yoga or walking in the evening can be more conducive to relaxation and preparing the body for rest. Finding a balance between staying active during the day and winding down in the evening can contribute to a more restful night’s sleep for individuals managing PTSD and insomnia.
Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on potential medication options for managing PTSD-related insomnia.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial when seeking guidance on potential medication options for managing PTSD-related insomnia. A qualified medical provider can assess your individual needs, discuss the benefits and risks of different medications, and tailor a treatment plan that aligns with your specific symptoms and overall health profile. Medication, when used appropriately and under professional supervision, can be an effective tool in addressing insomnia associated with PTSD, helping you achieve better sleep quality and overall well-being.