Understanding the Importance of Circadian Rhythm Sleep
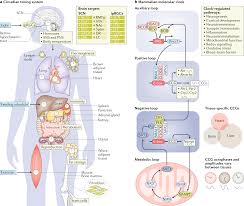
Our bodies are finely tuned machines that operate on a natural internal clock known as the circadian rhythm. This internal clock regulates various biological processes, including the sleep-wake cycle, hormone production, metabolism, and body temperature. The circadian rhythm is influenced by external factors such as light and darkness, which help synchronize our internal clock with the 24-hour day-night cycle.
One of the most critical functions of the circadian rhythm is to regulate our sleep patterns. Sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, playing a crucial role in physical and mental restoration. When our circadian rhythm is disrupted, it can lead to sleep disturbances and a host of health issues.
Research has shown that maintaining a consistent sleep schedule that aligns with our circadian rhythm can improve the quality of our sleep and overall health. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate our internal clock and promotes better sleep quality.
Disruptions to our circadian rhythm, such as jet lag or shift work, can have profound effects on our health. These disruptions can lead to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, and feeling rested upon waking. Chronic disruption of the circadian rhythm has been linked to an increased risk of various health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mood disorders.
To support healthy circadian rhythm sleep patterns, experts recommend establishing a bedtime routine that includes winding down before bed, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulants like caffeine close to bedtime, and exposing yourself to natural light during the day.
In conclusion, understanding and respecting our circadian rhythm is vital for maintaining optimal health and well-being. By prioritizing healthy sleep habits that align with our internal clock, we can improve the quality of our sleep and enhance our overall quality of life.
Understanding Circadian Rhythms: Answers to Common Sleep Cycle Questions
- How do I fix my sleep circadian rhythm?
- What is the circadian rhythm of sleep schedule?
- What is the best circadian rhythm for sleep?
- What is the best time to sleep for circadian rhythm?
- What happens when your circadian rhythm is off?
- What is a circadian sleep rhythm?
- What are the 4 circadian rhythms?
How do I fix my sleep circadian rhythm?
Fixing your sleep circadian rhythm involves establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a bedtime routine that aligns with your body’s natural internal clock. Start by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your circadian rhythm. Create a relaxing pre-sleep routine that includes activities like reading, meditating, or taking a warm bath to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. Avoid stimulants like caffeine and electronics close to bedtime, as they can disrupt your ability to fall asleep. Additionally, expose yourself to natural light during the day and keep your bedroom dark and cool at night to support healthy sleep patterns. By making these adjustments and prioritizing good sleep hygiene, you can help reset and optimize your circadian rhythm for better quality sleep.
What is the circadian rhythm of sleep schedule?
The circadian rhythm of sleep schedule refers to the body’s internal clock that regulates the timing of sleep and wakefulness over a 24-hour period. This natural biological rhythm is influenced by external factors such as light and darkness, helping to synchronize our sleep patterns with the day-night cycle. A consistent circadian rhythm of sleep schedule involves going to bed and waking up at the same time each day to maintain a healthy sleep-wake cycle. By aligning our sleep habits with our circadian rhythm, we can improve the quality of our sleep, enhance overall health, and promote optimal functioning of various bodily processes.
What is the best circadian rhythm for sleep?
Finding the best circadian rhythm for sleep involves aligning your bedtime and wake-up time with your body’s natural internal clock. While individual sleep needs vary, experts generally recommend aiming for a consistent sleep schedule that allows for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. The ideal circadian rhythm for sleep typically involves going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to maintain a stable internal clock. It’s important to listen to your body’s signals and adjust your sleep routine accordingly to ensure you are getting enough restorative sleep in harmony with your circadian rhythm.
What is the best time to sleep for circadian rhythm?
Determining the best time to sleep for optimal circadian rhythm alignment is a common question among individuals seeking to improve their sleep quality. The answer varies from person to person, as each individual’s circadian rhythm may differ based on factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and age. Generally, experts recommend aiming for a consistent sleep schedule that aligns with your natural body clock. For most adults, the ideal bedtime falls between 10:00 PM and midnight, with waking up around 6:00 AM to 8:00 AM. This timing allows for adequate restorative sleep cycles and synchronization with the body’s internal clock. However, it’s essential to listen to your body’s signals and adjust your sleep schedule accordingly to find the best time that works for you and promotes a healthy circadian rhythm.
What happens when your circadian rhythm is off?
When your circadian rhythm is off, it can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being. Disruptions to your internal clock can lead to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, and waking up feeling refreshed. An irregular circadian rhythm can result in sleep disturbances, fatigue, mood swings, decreased cognitive function, and impaired immune function. Chronic disruptions to your circadian rhythm have been linked to an increased risk of various health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mental health disorders. It is essential to prioritize healthy sleep habits and maintain a consistent sleep schedule to support the proper functioning of your circadian rhythm and promote optimal health.
What is a circadian sleep rhythm?
A circadian sleep rhythm refers to the natural, internal clock that regulates our sleep-wake cycle based on a 24-hour day-night cycle. This rhythm is controlled by the brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus and influenced by external factors such as light and darkness. A healthy circadian sleep rhythm helps us maintain consistent and restful sleep patterns, ensuring that we feel alert and energized during the day and sleepy at night. Disruptions to this rhythm, such as irregular sleep schedules or exposure to artificial light at night, can lead to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, and feeling rested upon waking. Prioritizing a consistent bedtime routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment can help support a balanced circadian sleep rhythm for improved overall health and well-being.
What are the 4 circadian rhythms?
The circadian rhythms refer to the natural, internal processes that follow a roughly 24-hour cycle and regulate various physiological functions in our bodies. There are four main circadian rhythms that play a crucial role in our daily lives: the sleep-wake cycle, the body temperature rhythm, the hormone secretion rhythm, and the mental alertness rhythm. The sleep-wake cycle is perhaps the most well-known circadian rhythm, governing when we feel sleepy and when we feel awake. The body temperature rhythm fluctuates throughout the day, with our temperature typically being lowest during sleep and highest in the late afternoon or early evening. Hormone secretion rhythms control the release of hormones like cortisol and melatonin, influencing our energy levels and sleep patterns. Lastly, the mental alertness rhythm dictates when we are most mentally sharp and productive during the day. Understanding these four circadian rhythms can help us optimize our daily routines for better health and well-being.